Analysis/Recommendations
Network Access - Analysis/Recommendation
With regards to Information Infrastructure, Internet Availability, Network speed and Quality, Hardware and Software, Service and Support Malaysia is at stage 3. With regards to Internet Affordability, Malaysia is transitioning out of stage 2 and into 3. There are some challenges that need to be addressed for Malaysia to emerge at stage 4, which is the goal of its Vision 2020 plan. These challenges include, opening up its telecom infrastructure to private industry to foster competition in products, prices, and services.
Networked Learning - Analysis/Recommendation
With regards to School's Access to ICTs and Enhancing Education with ICTs, Malaysia is at stage 3 and developing towards stage 4. This is evident as more primary and secondary schools have started to produce rich multimedia web pages. Setting a minimum technical educational standard for all teachers is a great stepping stone for stage 3. With regards of Developing the ICT Workforce, Malaysia is at stage 4 and solidifying. Many universities have started to offer complete degrees online for distant learning. This along with much investment in technical education by private institutes is fueling Malaysia to solidify its self at stage 4
Networked Society - Analysis/Recommendation
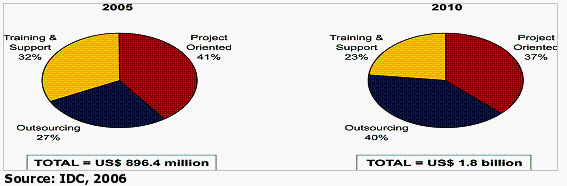
Our analysis shows that Malaysia is well on its way to becoming a powerhouse in the arena of network readiness for developing countries. In fact, IDC has identified significant opportunities in Malaysia for services from now until 2010.
Malaysia IT Services Spending in 2005 vs. 2010, by Macromarket (%)
toward this end.Malaysia in terms of "Networked Society" using the Readiness for the Network World would fall under Stage 4.
Networked Economy - Analysis/Recommendation
Malaysia's networked economy is very advanced due to its recognition of the need to use technology to advance its standing in the global economy. The government's focus on evolving to a knowledge based economy has caused it to develop specific programs
ICT Employment Opportunities B2C Electronic Commerce B2B Electronic Commerce E-Government A significant number of employees in the community require technical skills to perform their jobs.
A sizeable portion of the community's economy is based on the management of and trade in information, employing a large number of knowledge workers.
Information and communication technologies are considered central to the strategies of many organizations. Many businesses in the community have incorporated the World Wide Web into their sales, marketing, and customer service systems. The total volume of online retail is a noticeable component of the community's commercial activity, as may be evidenced by advertisements for commercial websites in traditional media and other indicators
Many efficiencies in B2B transactions are apparent as a result of the deployment of electronic systems. These efficiencies have changed market structures and redefined industry practices.
Many businesses have incorporated the Web into sales, procurement and inventory management. Some transactions occur online over automated, fully-integrated systems.
Order processing and delivery may be executed electronically and monitored through online tracking systems.
Overall levels of electronic B2B transactions are a noticeable and growing percentage of total B2B transactions within th e community.
All governmental agencies post key information on websites and some have incorporated the Web into their strategy for interaction with the public.Interactive government websites allow the public to conduct transactions (e.g. apply for permits, pay taxes) online.
Much government procurement and many interactions with suppliers take place online or with other electronic mediation. STAGE 4
Network Policy - Analysis/Recommendation
Our Analysis indicates that Malaysia has developed the guidelines and frameworks to address and improve processes within the Network Policy quadrant. The government's involvement and establishment of key governmental agency was key factor in making Malaysia a global leader. We also feel that at the end of Ninth Malaysia Plan, 2006 - 2010 will make the country a strategic partner. Malaysia in terms of "Network Policy" using the Readiness for the Network World would fall under stage 4. Malaysia's ability to be in this stage was due to the government's involvement in establishing infrastructure improvements to make Malaysia a competitive force. In 1998 the government created"The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission Act"under The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission. In conclusion, our recommendation is to stay the course on what"The Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission" has layout per the Framework for Industry Development (FID). This framework has addressed all gaps that will improve the countries regulatory policies. As for corporations entering Malaysia, they will find government agencies that will provide all the details for a successful entry into the countries economic backbone.
Offshore Opportunities - Analysis/Recommendation
Malaysia has made great advancements in becoming a strategic offshore provider. This was fueled by the government and its projects to improve infrastructure and attract corporation in making Malaysia an option in offshore services. These services started with engineering of semiconductors to providing back office services. In conclusion, Malaysia has proven to the business world it is capable of handling offshore services and providing talent to grow a company's strategic vision. Our recommendations for offshore outsourcing to Malaysia will be via the major consulting firms currently established in the country. These are large consulting companies with US roots and ability to bridge any gaps between organizations, cultural and business.