Network Access - Analysis
Information Infrastructure
The 2003-2004 Global Information Technology report ranked Malaysia the highest for an Asian developing country and ranked Malaysia as second for largest improvements in the World Competitiveness report. The Vision 2020 plan is guiding the stimulation of the telecom industry in Malaysia, by the government, to achieve the status of Malaysia as a developed country by 2020.
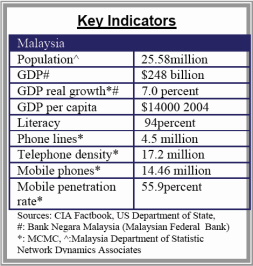
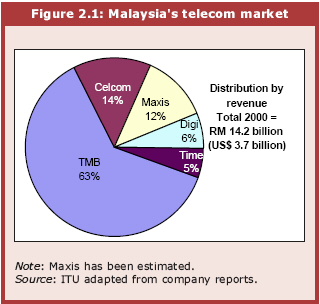
There are only a few players in the telecom market and Telekom Malaysia Berhad (TMB), a government backed telecom provider, has by far the largest market share4. For the private sector, the barrier to entry is high and lacks government encouragement. 4
Internet Availability
In 2005, it was estimated that Malaysia has 11.016 million internet users2. An earlier study found that while urban areas have access to higher internet speeds, the rural population has access to less than 56 kbps, as show below1. Broadband access remains low, at below 1 percent in 20043. This is a fairly low number when compared to the resources and energy committed to stimulate the telecom sector3.
Access to the Internet in Urban Areas1
| More than 256 kbps | Less than 256 kbps | Less than 56 kbps | |
| Bangladesh | X | ||
| Brunei Darussalam | X | ||
| Cambodia | X | ||
| China | X | ||
| India | X | ||
| Indonesia | X | ||
| Lao People's Democratic Republic | X | ||
| Malaysia | X | ||
| Mongolia | X | ||
| Myanmar | X | ||
| New Zealand | X | ||
| Pakistan | X | ||
| South Korea | X | ||
| Sri Lanka | X | ||
| Thailand | X | ||
| Vietnam | X |
Access to the Internet in Urban Areas1
| More than 256 kbps | Less than 256 kbps | Less than 56 kbps | |
| Bangladesh | X | ||
| Brunei Darussalam | X | ||
| Cambodia | X | ||
| China | X | ||
| India | X | ||
| Indonesia | X | ||
| Lao People's Democratic Republic | X | ||
| Malaysia | X | ||
| Mongolia | X | ||
| Myanmar | X | ||
| New Zealand | X | ||
| Pakistan | X | ||
| South Korea | X | ||
| Sri Lanka | X | ||
| Thailand | X | ||
| Vietnam | X |
Internet Affordability
On average, internet for residential and business users isn't cheap; in many areas, coverage is limited. The mean monthly gross income, which has gone up year over year, in US dollars is $800 per month6 and when currency is converted to US dollars, here are the internet rates.
Residential5:
Wired: $6/month - $55/month
Wireless: $55/month - $80/month
Satellite: $45/month - $250/month
Commercial5:
Wired: $120/month - $340/month
Satellite: $100/month - $250/month
Network Speed and Quality
Network quality and speed are a direct function of where one is location in Malaysia. Urban areas have access to faster speeds via wire, wireless, or satellite. Rural locations lag far behind and have very limited access to speed or good quality. Specifically, PSTN/ISDN dial-up access and ADSL/SDSL access are widely available in urban areas.
Hardware and Software
Major hardware, software and consulting firms have expanded to Malaysia, such as, IBM, Microsoft, CSC, Sun, and HP. Some are providing solutions for consumers while others are providing end-to-end solutions for businesses in Malaysia.
Service and Support
Offshore support and service to Malaysia is becoming more of a trend. Best practices from offshoring to countries like India are being applied to offshore to Malaysia. In July of 2006, HP had to defend its move to offshore some of its support to Malaysia7. Dell has moved part of its support team from India to Malaysia earlier in 2006. New ISPs have recently emerged in the market to provide competitive rates and web related services.