|
| Introduction |
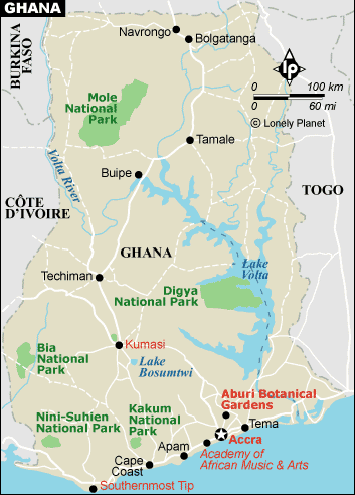 Formed
from the merger of the British colony of the Gold Coast and the Togoland
trust territory, Ghana in 1957 became the first sub-Saharan country
in colonial Africa to gain its independence. Ghana is located on the
West Coast of Africa, 50 km north of the equator on the Gulf of Guinea.
The capital, Accra, lies on the Greenwich Meridian. The coastal area
consists of plains and numerous lagoons near the estuaries of rivers
and the land is relatively flat. The climate is tropical, characterized
by moderate temperatures for most of the year (21-32 °C), constant
breezes and sunshine, with two rainy seasons, between March-July and
September- October. The population of Ghana is estimated to be 20.7
million, with 38% of the population under the age of 15 years. The
population density averages 86 persons per square km, with most of
the population concentrated in the southern part of the country -
with highest densities in the cocoa-producing areas. Formed
from the merger of the British colony of the Gold Coast and the Togoland
trust territory, Ghana in 1957 became the first sub-Saharan country
in colonial Africa to gain its independence. Ghana is located on the
West Coast of Africa, 50 km north of the equator on the Gulf of Guinea.
The capital, Accra, lies on the Greenwich Meridian. The coastal area
consists of plains and numerous lagoons near the estuaries of rivers
and the land is relatively flat. The climate is tropical, characterized
by moderate temperatures for most of the year (21-32 °C), constant
breezes and sunshine, with two rainy seasons, between March-July and
September- October. The population of Ghana is estimated to be 20.7
million, with 38% of the population under the age of 15 years. The
population density averages 86 persons per square km, with most of
the population concentrated in the southern part of the country -
with highest densities in the cocoa-producing areas.
|
| Social |
There are nine principal ethnic groups (Akan,
Guans, Ewes, Dagombas, Gas, Gonjas, Adages, Walas and Frafras), at
least 56 dialects. The official language is English, with French and
Hausa being the two major foreign languages spoken in the country.
There are three main religions in Ghana: Christians (43 per cent),
animists (38 per cent) and Muslims (12 per cent). There is complete
freedom of religion. There are numerous educational institutions in
Ghana that have helped to reduce the illiteracy rate to 22 per cent
for male and 40 per cent for females.
|
| Politics |
A new constitution was introduced in 1992 following
11 years of military rule. Multi-party elections were held shortly
thereafter and in 1996. The National Democratic Party won both. In
2000 the Government of the National Democratic Congress lost to the
opposition New Patriotic Party (NPP). Ghana had enjoyed a smooth third-term
election, conducted with full participation of all political parties
and of the Ghanaian electorate, strengthening the democratic institutions.
The World Bank has played an active part in Ghana¡¦s
economic recovery. With 32 active projects, the country portfolio
is the largest in Africa and current commitments amount to over USD
1.4 billion.
|
| Economy |
Well endowed with natural resources, Ghana has
roughly twice the per capita output of the poorer countries in West
Africa. Even so, Ghana remains heavily dependent on international
financial and technical assistance. Gold, timber, and cocoa production
are major sources of foreign exchange. The domestic economy continues
to revolve around subsistence agriculture, which accounts for 35%
of GDP and employs 60% of the work force, mainly small landholders.
Ghana opted for debt relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor Country
(HIPC) program in 2002. Policy priorities include tighter monetary
and fiscal policies, accelerated privatization, and improvement of
social services. Receipts from the gold sector should help sustain
GDP growth in 2004. Inflation should ease, but remain a major internal
problem.
| Population |
20.7 million |
| GDP per capita |
$2,200 |
| GDP growth rate |
4.7% |
| Life expectancy |
56.27 |
Literacy
|
74.8% |
|
| |

 Formed
from the merger of the British colony of the Gold Coast and the Togoland
trust territory, Ghana in 1957 became the first sub-Saharan country
in colonial Africa to gain its independence. Ghana is located on the
West Coast of Africa, 50 km north of the equator on the Gulf of Guinea.
The capital, Accra, lies on the Greenwich Meridian. The coastal area
consists of plains and numerous lagoons near the estuaries of rivers
and the land is relatively flat. The climate is tropical, characterized
by moderate temperatures for most of the year (21-32 °C), constant
breezes and sunshine, with two rainy seasons, between March-July and
September- October. The population of Ghana is estimated to be 20.7
million, with 38% of the population under the age of 15 years. The
population density averages 86 persons per square km, with most of
the population concentrated in the southern part of the country -
with highest densities in the cocoa-producing areas.
Formed
from the merger of the British colony of the Gold Coast and the Togoland
trust territory, Ghana in 1957 became the first sub-Saharan country
in colonial Africa to gain its independence. Ghana is located on the
West Coast of Africa, 50 km north of the equator on the Gulf of Guinea.
The capital, Accra, lies on the Greenwich Meridian. The coastal area
consists of plains and numerous lagoons near the estuaries of rivers
and the land is relatively flat. The climate is tropical, characterized
by moderate temperatures for most of the year (21-32 °C), constant
breezes and sunshine, with two rainy seasons, between March-July and
September- October. The population of Ghana is estimated to be 20.7
million, with 38% of the population under the age of 15 years. The
population density averages 86 persons per square km, with most of
the population concentrated in the southern part of the country -
with highest densities in the cocoa-producing areas.