| Overview |
| Network Access |
| Network Learning |
| Network Society |
| Network Economy |
| Network Policy |
| Offshore Opportunity |
| Conclusion |
 |
|||||
|
|
||||
| Introduction | ||||
| The A.T.
Kearney’s 2004 Offshore Location Attractiveness Index report
outlines key issues CEOs must consider when making offshore decisions.
The most attractive locations share common attributes. They have a
large, educated labor pool, a stable economic environment and a high
degree of global integration. Decision makers want to avoid such risks
as, incidents of intellectual property piracy, poor language skills,
and an unstable financial environment. There are also some basic guidelines
to use when identifying what process to outsource. Gartner provides
a model for assessing process suitability. If a process is highly
scalable and simple, it is a primary candidate for off shoring. |
||||
| Readiness | ||||
| Ghana is in the earliest stages of outsourcing.
Public funding for technology training in primary or elementary levels
is scarce. Despite their interest and desire to increase computer
learning, lack of early and continuing education puts them at a distinct
disadvantage for outsourcing, in comparison to more mature markets
like India or China, for example. In order for Ghana to raise its
attractiveness it must “raise educational standards, invest
in research, provide more extensive training, and promote their ICT
industries at both state and national levels”, according to
A.T. Kearney. The technology and programming skills being taught in
universities is not innovative, it is outdated. Students leaving college
with Assembler and COBOL skills are not as marketable as those having
C++ or other 3rd generation languages. With a Network Access ranking of Stage 2, Ghana’s infrastructure exists but is not mature enough to support wide-scale outsourcing. Price, regulation and stability must be fully addressed before Ghana can be ready to absorb programming work from other countries as an offshore provider. |
||||
| Attractiveness | ||||
| According to the article Outsourcing
Excellence: Looking Beyond Low Wages, “The essential concepts
behind outsourcing are quality of work and the effectiveness of business
processes. Placing certain functions in the hands of a specialist
is the best way to get constant and focused attention to making improvements
on the effectiveness of these processes.” They go on to say
“the key strategy involved in moving offshore should be based
on the competitive advantage of the country in question.” There is a possibly Ghana could capitalize on the skills of their labor pool, by outsourcing exclusively to companies who have large legacy systems to feed and support. However, the legacy system market is not growing. In this scenario, countries who keep technical education at the leading edge will out compete Ghana. Ghana cannot compete on price alone. They need to couple competitive pricing with an expanded base of service offerings. Additionally, Ghana’s brain drain problem will remain an obstruction to their ability to outsource effectively. Brain drain is a major hazard for any country trying to get into the outsourcing business. It happens when skilled intellectual and technical labor moves to more favorable geographic, economic and professional environments. The Net effect to Ghana is a depletion of valuable human resource. |
||||
| Conclusion | ||||
| Throughout the world one will find leaders,
contenders and rising stars in the offshore marketplace. Ghana is
a rising star. All destinations possess some characteristics that
attract companies to its shores. There is not a one size fit’s
all strategy in selecting a site. India will continue to dominate
the offshore market, China is close behind. Other sites, like Ghana,
boast strong English language skills or technical qualifications,
but weak economies and infrastructures. The type of work to be sent
offshore, price, quality measurements and scalability needs are all
factors to be considered. Choosing an offshore site is as much an
exercise of searching for the geographic location as it is of determining
suitability, scalability and complexity of the task to be outsourced. Ghana’s outsourcing asset include: Ghana’s challenges: Ghana’s as an area for outsourcing falls under the category of Medium attractiveness and low readiness. Offshore Readiness vs. Attractiveness 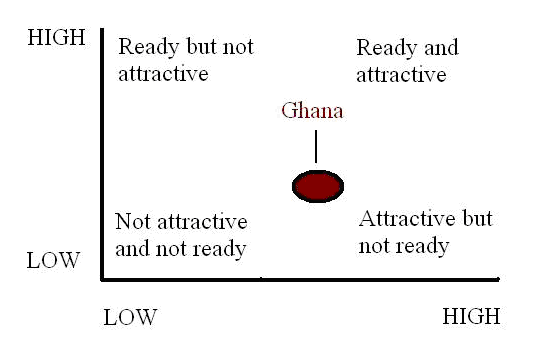 |
||||