Home Background Network Learning Networked Society Networked Economy Network Policy Offshore Opportunities Conclusion References
Network Access
Information Infrastructure (Stage 3)
Argentina’s current network infrastructure allows a majority of the community access to telephony and Internet services. At the turn of the century, usage of advanced technology was beginning to progress. However in 2001, Argentina experienced major economic hardships that caused the progression of technology usage to be stifled. Currently, Argentina is bouncing back from those economic hardships. Internet, mobile phone, and computer usage has increased drastically since then. In 2005, Argentina mobile phone subscriptions increased by 68% to 22.02 million [7]. In other words, there were approximately 57 mobile phones per 100 people in 2005. In 2006, that number increased again to approximately 68 mobile phones per 100 people. [8] In 2004, roughly 30% of Internet usage was made through public facilities (i.e., Internet cafes), which is a leading indicator that Internet service is not only made available to the wealthy or within limited households [10]. However, one problem in Argentina is that the poorest areas do not have adequate access to the Internet and fixed telephony services. The government is currently using incentives to encourage the telecommunication companies to provide adequate telecommunication services to poor areas. Currently, many of those individuals in the poorer communities utilize mobile phones as their only means of communication. The teledensity in Buenos Aires is 37%; however, the teledensity for most of the other provinces are less that 20%. [9]
In 2006, there were 8.88 million main lines, which is an increase of 1.6% when compared to 2005. This is a teledensity of approximately 22 mainlines per 100 people. However, local call volume decreased by 0.4%. This can be attributed to the increase in mobile phone usage. [7]
Argentina is currently in stage 3 of Internet Infrastructure due to the fact that there are between 20 and 40 mainlines per 100 people. Additionally, there is a significant increase in mobile phone usage, which is a sign of an increased telecommunications usage. In 2005 and 2006 there were drastic changes towards the use of mobile phones. The usage of mobile phones increased 68% in 2005 and 19% in 2006. To move to stage 4 Argentina needs to significantly increase mainline availability and maintain steady growth in mobile phone subscriptions.
Internet Availability (Stage 3)
Internet availability throughout Argentina is wide and usage has been significantly increasing over the past couple of years. Internet usage statistics indicate that there are approximately 13 million Internet users in Argentina. The statistics indicate that the Internet is accessed in the following methods:
Another statistic that is important to note is that 90% of the broadband usage is in the provinces of Buenos Aires, Santa Fe, Córdoba and Mendoza. [11]
As of 2006, growth of wireless internet usage has been slow in all of Latin America including Argentina. The usage of 3G wireless, WiMAX, and wireless hotspots are currently in the trial phases. [12]
The three primary Internet service providers (ISPs) in Argentina are Telefónica de Argentina S.A. (TASA), Impsat Fiber Networks and Telecom Argentina [13]. As of 2000, there were approximately 33 ISPs in Argentina, which is 0.825 ISPs per 1,000,000 people. [14]
Argentina is at stage 3 for Internet Availability. Argentine citizens have adequate access to the Internet. This access includes wireless, broadband, cable, DSL, satellite, and dial-up access to the Internet. Additionally, Argentina’s telecommunication companies provide web hosting services and free Internet solutions to the public for personal and business use. The primary reason that Argentina is at a stage 3 is that broadband subscriptions are less than 5% of the total population, 90% of the broadband usage are in the provinces of Buenos Aires, Santa Fe, Córdoba and Mendoza, and only one-third of the Argentine population uses the Internet. To move into stage 4, access to Internet services, specifically broadband usage, will need to increase in the non-major provinces throughout Argentina. Additionally, the number of ISPs in Argentina has to more than double.
Internet Affordability (Stage 3)
There is a direct correlation with Internet availability and Internet affordability within Argentina. As the Internet use increases, the Internet cost decreases. Based on the World Bank analysis of Argentina ICT at a glance, Internet service has averaged $14.40/month (US) compared to other Latin American countries which are at $25.80/month. Argentina is relatively priced lower for Internet affordability within upper-middle-income groups, which have an average of $17.00/month. The affordability of fixed lines was reported as $6.80/month in 2005 compared to $20.00/month in 2000. Argentina is relatively priced lower for fixed phone lines within upper-middle-income groups, which have an average of $12.10/month. [15]
A comparison of different services offered by the 3 major telecommunication giants in Argentina provided the following:
Based on the comparison performed by Gartner and the analysis by World Bank, Argentina appears to be a Stage 4 for Internet affordability. The pricing strategies cross over to the corporate and consumer markets with numerous options for the user to select. Bandwidth options are offered which tiered accordingly to the speed of access. Lastly, the 3 top telecommunication vendors in Argentina offer several solutions for consumers.
[15]
Network Speed and Quality (Stage 3)
Argentina’s quality of lines has increased over time. The fixed –line telecommunications improved in both the quality and coverage within the country. With the expansion and popularity of the Internet, the speed and overall quality had to expand in order to keep up with the current technologies. The World Bank rated the quality of telephone faults at 21.2 per thousand people in 2005. The broadband subscribers significantly increased as it was measured at 21.7 per thousand in 2005, from 2.3 per thousand in 2000. The increase in broadband as brought an increase in speed. [15] International Internet bandwidth was measured at 12 bits per person in 2000, to 316 bits per person in 2005. An analysis of the packet transmission was performed and resulted in an average of 1% in packet loss within Argentina. [17]
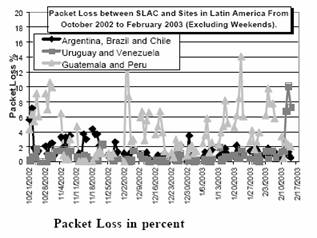 [17]
[17]
Argentina is at stage 3 for Network speed and Quality. Although, the speed has increased over the past years, adequate backbone capacity is not consistently administrated throughout Argentina. As Gartner reports, the main problem racing ISPs in Argentina is the capacity connections. In order for Argentina to move into a stage 4, they will need to increase the satellite services and fiber network connectivity. [16]
Hardware and Software (Stage 3)
In 2005, Argentina had approximately 85 personal computers for every 100 citizens. This may seem appropriate, but per Gartner studies the worldwide average at the time was 123 computers for every 100 citizens. Other Latin American countries like Mexico and Brazil have 117 and 121 computers per 100 citizens respectively and the average for mature markets is 624 computers per 100 citizens. At the time of the study, there were four phases of maturity regarding PC penetration: Emerging Markets 1, Emerging Markets 2, Mature Market1, and Mature Market 2. Argentina was considered to be in the Emerging Markets 2 phase. [18]
The lack of maturity can be attributed to the 2002 Argentine market collapse, which slowed down much of Argentina’s economy. During 2002, computer sales were significantly impacted due to the economy. Sales decreased by 77% in 2002. However, since 2002 computer sales have been increasing. [19] During 2005 and 2006 computer sales, PC sales were over 859,000 [8] and 1,500,000 respectively. [19] In 2006, computer sales increased by 39% [19], thus increasing the ratio of personal computers to people to 111 personal computers to 100 people. Most of those computers were produced in Argentina. [20]
Argentina is currently in stage 3 of Hardware and Software. There is a wide variety of hardware and software available in Argentina and most of the purchased computers were produced in Argentina. However, to move into stage 4 there needs to be a higher ratio of computers to people. The number of computes per 100 people needs to be much closer to those of mature markets.
Service and Support (Stage 3)
Based on Gartner’s research of network and Internet services in Argentina, the service and support appears adequate to rate this section at stage 3. The following reasons justify the rating:
In order for Argentina to move into a stage 4, the mainline availability needs to be increased in the timing for users to obtain new services. Wait lists are still used to reserve mainlines in Argentina, which can result in several weeks before obtaining a main line. The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) produced a study of countries e-readiness, which is a measurement of a countries ability to adapt to an e-business environment (i.e., how amenable a market is to Internet-based opportunities). As listed in the table below, Argentina is rated 39 out of 65 countries in the ability to support e-business related services. [21]
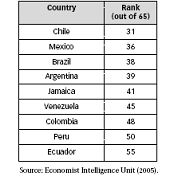 [21]
[21]