Network Access
Information Infrastructure: Stage 3
The telecommunication market was open to private sector by the late 90’s. Many
private companies around the world invested in the telecommunication
infrastructure of the country. As a result the communication infrastructure in
the country has improved tremendously. Also, Due to its unique location in
Central America the Republic of Panama is considered the hub of Latin America.
There is five of the major fiber-optic cables systems meets in Panama.
As an example, the Americas Region
Caribbean Ring System (ARCOS-1), the MAYA-1, and PAN-AM submarine cable systems
provide links to the US and parts of the Caribbean, Central America, and South
America.
According to the CIA World Factbook the Republic of Panama has 537,100 telephone
land lines is use (2010 report). This is low for stage 3 country, but the
wireless communications makes up for the telephone shortage. The CIA Factbook
indicates that in 2010 there were 1,352,000 subscribers for a population of
3,600,000. There are multiple private owned networks, government owned TV
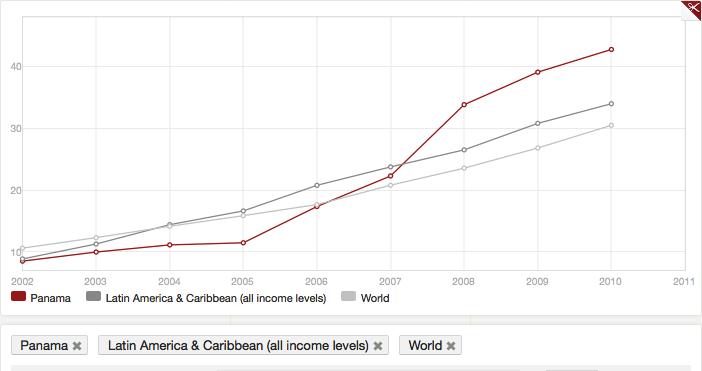
stations, and cable & satellite services are available. The graph below shows
the number of Internet users (per 100 people) in comparison to Latin America in
average.
Internet Availability: Stage 3
There are 7,149 Internet service providers to support 300,000 users. The
internet market was open for private sector in 1997. Since then many companies
invested in improving the availability of their service to cover more users and
areas. The internet is available in the Republic of Panama through a number of
choses. There are the DSL companies which uses the landline for connection.
Also, we have the cable MODEM high-speed companies that provide individuals as
will as businesses with over 10Mbps. In addition to the two previous types,
there is the mobile Internet service which is not very fast but accessible. The
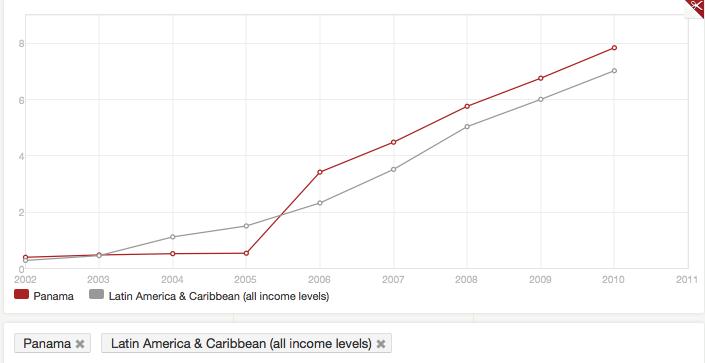
graph below, from the world’s bank database, shows the number of
subscribers for high speed Internet (per
100 people).
As of May 18th, 2011 there are 655 access points in 22 cities allover
Panama. These access points located in schools, city halls, community clubs,
libraries, health centers and hospitals. Panama also has a wide variety of
internet cafes or cybercafés where people can use the internet and pay for the
use. Many companies use hot spot in public places like the airports and
restaurants. Because the internet availability still is lacking in some rural
parts of the country a stage 3 would be appropriate for the Republic of Panama.
Internet Affordability: Stage 3
The telecommunication companies provide a variety of services and prices below
is a list of Panama’s biggest ISP companies along with their price and service:
Cable & Wireless: is a British company walked into the seen by 1997 providing
communication technologies to the Republic of Panama. The list below shows rates
based on type:
1 Mega Ilimitado: $14.95
2 Mega Ilimitado: $16.95
3 Mega Ilimitado: $24.95
4 Mega Ilimitado: $29.95
5 Mega Ilimitado: $42.95
Cable Onda (speed – price ): is an internet service does not occupy the
landline, unlike the DSL service. At
the maximum speed it is faster than DSL for home users and up to 43 times faster
than dial-up connection. Onda charges $11.96 per month for unlimited calls
nationwide which is about the same prices as Cable & Wireless.
The charge for 4 MB speed internet is
$28.95 which is slightly less than the cost for Cable & Wireless
Movistar: for $39.95 a month the user get to enjoy the Internet whenever
wherever with a mobile Internet connection. The maximum speed for this kind of
Internet access is 153kbps, and it is getting faster with new technologies. An
eighteen months contract is required to get this service.
A Stage three was chosen for Internet affordability even though rates are
similar to the rates in the United States. The average income for people in the
USA is way more the average in Panama. Therefore, the Internet prices in Panama
would need to be a little cheaper to move to a better stage.
Network Speed and Quality: Stage 3
As mentioned previously, there are four international connections via
high-bandwidth fiber network that meets in Panama. As a result the individuals
and businesses get to enjoy a very good communications in terms of successful
call rates, connection drops, and Internet speed. The Telecommunication
infrastructure of Panama is capable of meeting the demands of the market.
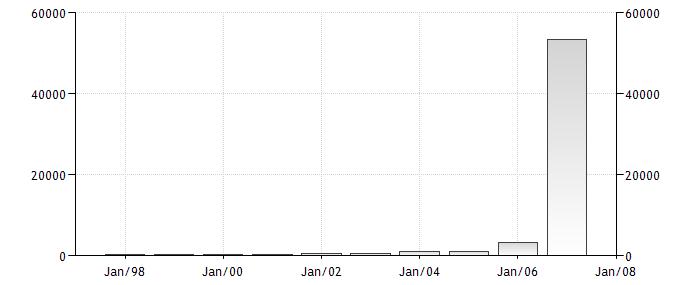
According to the CIA World Factbook, in 2004 the international Internet
bandwidth was over 926Mbps. Placing it #56 in terms of bandwidth. The figure
below shows the international bandwidth of Panama From 1998 until 2008.
A stage three was appropriate for the reasons mentioned above. Also, The
Internet speeds are fast, but not as fast as stage four countries where the
speed for individuals reaches 50 MB. So Panama need to work on better
fiber-optic local infrastructure to reach stage four.
Hardware and Software: Stage 2
Software and hardware development and research is not well developed in the
county. There are limited or no local options for hardware or software.
There are two factors that may help to increase the amount of production and
distribution in Panama which include the government’s electronic initiate to
increase the computer and internet presentation in the country and the
development of the Panama-Pacific special Economic Area which seeks to seek to
attract the companies to the region.
Panama was placed at stage two because it has some ICT, but not enough to
support the country needs. According to the worlds bank the total ICT % of all
goods imported has decreased from 9.4% in 2005 to 7.2% in 2009, but Panama
requires significant improvement in this area to move to stage 3. Additionally,
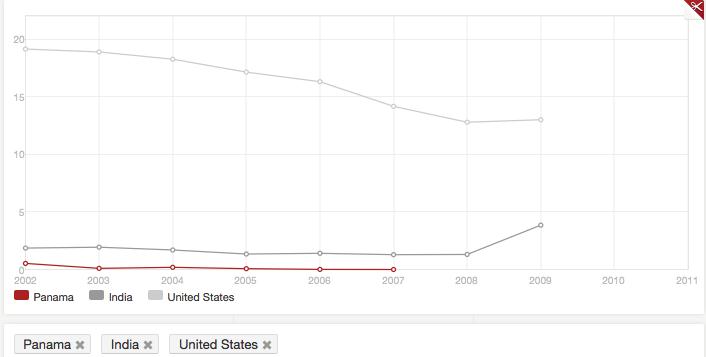
the graph below from the world’s bank data base shows that the exports from
Panama in ICT between 2003 and 2007 was around 0% of total export goods.
Service and Support: Stage 3
The Service and Support in Panama is at Level 3. This might be an advance stage
in comparison to other Latin countries in the area, but opening the market to
the private sector raised the competition between the companies to provide the
best service and support. It does not take to long to install telephone
landline; it takes no time to get Internet service. There are a growing number
of hardware technicians, web designers and network administrators.
Some problems that denied Panama a better stage are the fact that some
maintenance takes longer to complete,
installation in rural areas takes longer, Internet providers are not
clear about the rates and services, and there are not enough ICT local
businesses to support the local need.
|