Networked Society
People and Organizations Online (Stage 4)
The number of Internet subscriptions was an estimated 1,621,900 in 2009, a modest year-on-year increase of just over 2.4%, owing to the deep economic recession, which has cubed consumers' purchasing power. DSL users accounted for a 8.4% share of the internet subscriptions. The estimated amount of internet users is 7.7million for 2014 or about 77% of the popualation, since these also include users in internet cafe’s and not necessary subscribers.
The following chart depicts how many users are estimated for the future.
Internet users is in the 1,000’s, Internet Penetration (or users) is per 100 people, Broadband subscriptions is in the 1,000’s, and Broadband Subscriptions is per 100 people in the fourth category.
Hungary Population - 10,005,000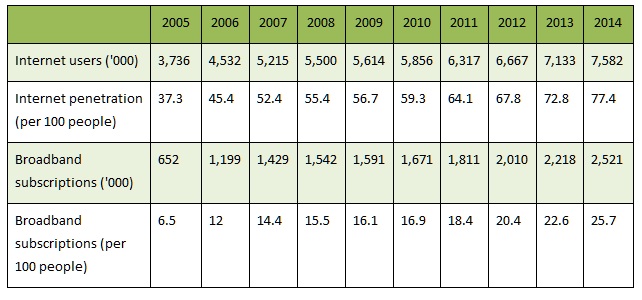
Reference and Source: 4.1
The mobile market is also very present in Hungary. Vodafone, T-Mobile, and Pannon GSM are the three main competitors in the industry. There are also approximately 89% of the population using cellphones as of 2005.
The following chart shows the respective mobile market and the competitors of the industry within Hungary
Source: http://www.andrastoth.hu/files/hungarian_telecom_regulation.pdf
Reference and Source: 4.2
There is also a growing trend in how many PCs are owned in Hungary relative to internet access. The following chart shows this trend of how many PCs there are compared to internet access. There is a surprising gap of computers without internet access.
Locally Relevant Content (Stage 3)
Hungary provides a few items for Hungarians to use. Having Governmental websites and Company websites is still a increasing trend in Hungary and is beginning to be more useful for users. Most users of the internet gain access at home, approximately 28.8% of users use it at home, this includes more than the subscriber of a household. The next biggest use of the internet is at work, which is around 18.7% of the internet users. The rest of the internet users access it at school or cyber cafes. Internet users do not generally access the internet for shopping or banking. This would prevent a few industries from coming to Hungary since there is little opportunity in some sectors. Most users use the internet and PCs for sending emails, looking up information on goods and services, playing games and music, and reading online newspapers and magazines. Only half of the governmental websites with public services are accessible. 4.3
Information & Communication Technologies in Everyday Life (Stage 3)
Only 10% of Hungarians have internet subscriptions. However, 5.7 million of the 10 million people in the population are using the internet on a daily basis. As stated above, the users that do use the computers use it for emailing, gaming, reading magazines and newspapers, and looking up information on products and services. Shopping and online Banking are only used by just a few of the internet users. There are a couple of restrictions that prevent more subscriptions. These restrictions are Access and Ability.
Access:
The restrictions in access are from telecom tariffs, in which the voice communications are expensive and internet access falls under this. The added price for the internet is in many times out of reach for the everyday citizen to be able to subscribe to the service. Some find that PCs are also too expensive still and that it is easier to just use an internet cafe for an hour a day or subscribe to an internet cafe for monthly use.
Ability:
There are many educational programs in Hungary to teach the interested people the elementary knowledge about computers and internet. The ability in Hungary for most of the population is lacking for simple abilities on the computer. Most people are not aware of Internet. Hungary is even implementing plans geared specifically for those who want to receive the minimal knowledge necessary for internet usage.
Reference: 4.4
On the other side of this, there is a growing trend of being an information society. In the European Union, people live by this, and it is growing in Hungary as well. The ability for people to access and culture of people wanting to access the internet in everyday life is evolving as it has in other EU countries. In an information society, there are three main functions that people live by:
- businesses and citizens must have access to an inexpensive, world-class communications infrastructure and a wide range of services;
- every citizen must obtain the skills needed to live and work in the information society;
- access to life-long learning is a basic component of the European social model.
These areas will only grow as more subscriptions and more users increase in Hungary.
Reference: 4.5
Information & Communication Technologies in the Workplace (Stage 3/4)
Companies that are looking at Hungary for a place for principal business are exceedingly becoming interested since the environment allows for freedom of information. The ICT workforce is increasing within Hungary as well and with the colleges teaching and studying ICT, it will only increase the quality of ICT within the country. The government has implemented multiple e-Government strategies to ICT in the workplace. In addition, multiple multinationals have set up offices in Hungary which include IBM, Microsoft, SAP and EDS. One specific example of ICT in the workplace is in the city of Pecs. The University of Pecs and surrounding hospitals communicate with an SAP ERP system. The long-term goal is to link hospitals around Hungary to one central ERP system. This hopes to improve transparency & accountability, improve collaboration, reduce redundancies, and ultimately cut costs.