|
Networked
Economy
In an effort to
achieve the Vision 2020 Agenda, Trinidad and Tobago(T&T)’s National
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Strategy, Fastforward, calls for
a transformation of T&T to a knowledge–based society. Critical occurrences for this transition
include the propagation of ICTs in business to support e-Commerce, e-Government,
and the increased use of related ICT services in business, thereby driving
greater economic competitiveness.
T&T has articulated an e-strategy that is clear in describing how
ICT development fits in with its nontechnology activities. The country’s ICT strategy explicitly states
its intention to contribute to the National Development Plan (“Vision 2020”) by
creating greater social equity through providing universal access to ICT. The e-strategy establishes a timetable and a
methodology to determine how the expansion of ICT in the country can be
leveraged to support economic, social, and environmental policy objectives.
ICT Employment Opportunities (Stage 2)
Because of the presence of large multi-national corporations
related to the natural gas and other industries, there is widespread advance
usage of ICT by small to large corporations in
T&T. However, corporations face a
shortage of skilled personnel to handle their local ICT development, which
often leads them to hire foreign staff for such needs.
The National Entrepreneurship Development Company (NEDCO) of
T&T’s objective is to “contribute to national development by empowering
individuals and communities to achieve financial independence”. NEDCO employs some 100 employees and is headquartered
in Port of Spain. NEDCO seeks to
strengthen capacity of smaller businesses by providing loans and other forms of
assistance.
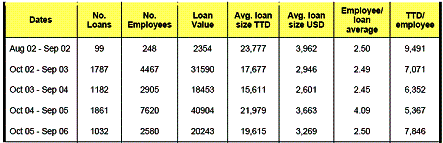
NEDCO has about 5,000 clients to which it has granted loans,
all of whom are Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). It views ICTs as important tools for
business and is assisting MSMEs to develop the necessary capacities for
employing these technologies for their competitive advantage. Because of the scope of its operations and
support for the use of ICTs as shown below NEDCO is making a major impact on
facilitating the adoption of e-Commerce in T&T as well as the concomitant
employment opportunities arising from such a process.
An incipient e-commerce industry and market have been
evolving timidly in the last few years.
A low penetration rate, the short distance to “real” providers, lack of
awareness and distrust on on-line business transactions are factors that affect
negatively the development of a local on-line business-to-consumers (B2C)
market. Consumers in T&T are not
yet demanding e-Commerce services.
Retail operations are not geared to the provision of e-Commerce. Many companies have simple websites that
offer browsing for consumers but there is extremely little in the way of
on-line sales functionality. The small
numbers of consumers who do visit company websites as part of the purchasing
process are primarily using it for price and product comparison, and are still
making the final purchase in a traditional manner.
There is however a significant market opportunity for
catering the interest of nationals living abroad on local products. In addition, the demand for e-Commerce
solutions from buyers and suppliers in T&T appears to be greatest in the
energy sector, where large companies such as BP demand that local businesses
use e-Commerce.
Business-to-business (B2B) Electronic
Commerce (Stage 3)
In recognition of the need for greater collaboration between
the public and private sectors in implementing fastforward, Government of
T&T established the e-Business Roundtable in 2006. The Round table comprises a mix of senior
Government officials, high-level business executives, technology experts, and
academics. The Roundtable acts as a
“think tank” for T&T’s economic growth and success by focusing on
leadership, opportunity recognition, innovation and revenue generation through
the use of ICTs in business. In
November 2008, in partnership with the e-Business Roundtable, the Government
hosted T&T’s first International ICT Business and Innovation Symposium, the
theme of which was “ICT: A Driver of National Transformation”.
EnterpriseNeTT, an online Business-to-Business (B2B)
Marketplace focusing on MSMEs was released as a pilot in 2007. As a companion to efforts aimed at
encouraging ICT adoption among MSMEs, EnterpriseNeTT launched Electronic
inter-bank Payments System. This
initiative by the Bankers Association of T&T (which groups all six major
banks operating nationally) and the Central Bank facilitates the
interconnection of local banks and paves the way for electronic and digital
payments. It improves the efficiency of
the banking system, with faster transfers and shorter funds clearance terms, as
well as enhanced monitoring and tracking.
Security is based on a combination of biometrics and encryption
techniques. In addition to facilitating
funds transfers among banks, the system lays the foundation and basic
functionality for Government and businesses to maintain electronic payrolls and
do electronic payments.
Use of ICT by medium sized businesses is common, although it
is mostly limited to the conventional applications for communication (e-mail,
web browsing, etc.), managing finances (accounting systems) and as support
business tools (spreadsheets, word processing and presentations). On the other hand, use of ICT among small
business is limited and is consistent with the low penetration rate of ICT.
At present, in T&T, there are few B2B e-Commerce
services. Online order fulfillment
takes place, but mostly with foreign B2C e-Commerce sites. Thanks to the efforts of the Government,
online content is increasing and will assist MSMEs in taking advantage of B2B
e-Commerce.
E-Government (Stage 4)
A robust, high speed Communications Backbone, GovNeTT,
currently connects 80% of Government Ministries, providing a secure platform
for inter-agency collaboration and integration. This Network was featured in the 2005 compendium of innovative
e-Government practices compiled by the United Nations Department of Social and
Economic Affairs (UNDESA). GovNeTT’s
imminent enhancements include the availability of VoIP, video-conferencing and
data centre services.
Consistent with broader public sector reform efforts, the
Government has been successfully introducing alternative channels of service
delivery as a means of becoming more customer focused, while at the same time
increasing its transparency, accessibility, availability, efficiency, and
effectiveness.
Under the national ttconnect initiative, citizens can
currently access Government through the Internet (ttconnect Online),
common counters (ttconnect Service Centre), and automated kiosks (ttconnect
Self Serve). While Government continues
to augment the service offerings of these channels, it is also extending the ttconnect
framework to include mobile (ttconnect On The Go) and contact centre (ttconnect
Hotline) channels.
The ttconnect online (www.ttconnect.gov.tt) was released to
the public in 2007 and currently provides online access to information on over
four hundred Government services and related resources; the first of this
magnitude in the English speaking Caribbean.
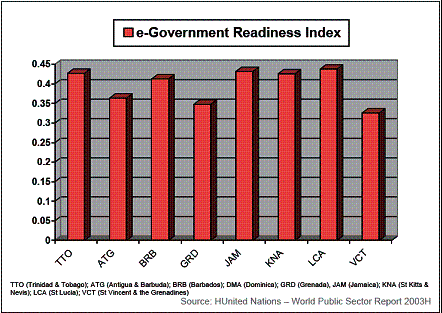
Shown below is the latest available e-Government readiness index
comparison between the T&T and other Caribbean countries.
| 


