Network
Access
Information Infrastructure – Stage
4
By the end of 2001, 62% of all Danish companies had created their
own home pages, an increase from 52% in just one year. Internet
service providers (ISPs) offer a full package of services and software,
including home pages, web design, browsers, e-mail, newsgroups,
search tools, and more. Denmark is a highly computerized and very
PC/LAN oriented market that is constantly growing. IT equipment
is relatively widespread in Denmark, both for private and public
use. Denmark is trying to develop “IT cities” and research
centers across the country. The city of Aarhus has been developed
as a literal IT-cluster named ‘Katrinberg IT City’,
which is full of research centers, incubation centers and IT business
undertakings. Denmark also has a very well developed communications
infrastructure that offers fully modern, nationwide coverage. In
addition, the Danish telecommunications systems are based on dominant
international standards and protocols. This is an essential prerequisite
for being able to efficiently "clone" products from one
market to another.
Internet Availability –
Stage 4
As of July 2002, 3,375,850 Internet Users or 62.5% of the Danish
population have access to the Internet according to Nielsen/Net
Ratings. Denmark is a country in which approximately one-third of
Danish people have broadband penetration. Currently there are one
million broadband connections in Denmark, which makes for a broadband
penetration of close to 40%. The frequency of Internet usage by
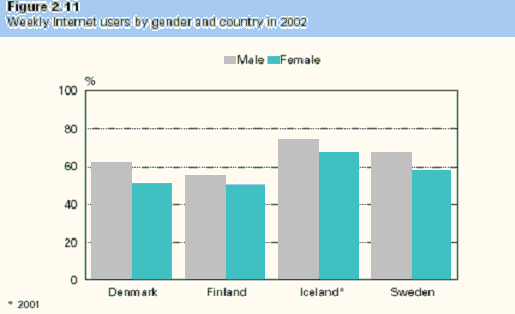
Danish companies is among the highest in Europe. In Denmark 65%
of Denmark males have access to the Internet; where as 58% of women
have access to the Internet.
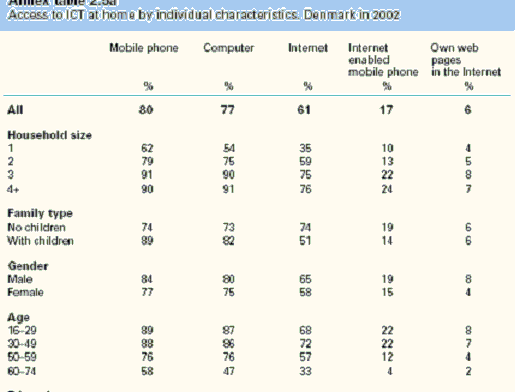
The more educated Danish people are, the higher the chances that they have Internet access. People in Denmark that have a post-baccalaureate education access the internet at 79%, where as people with a primary education access the internet at 44%. There is a large disparity between education and internet access in Denmark. The amount of access for a larger household tends to be higher for four or more people households, which is 85%. Where as one person households seem to access the network at 45%. Also, over 80% of Danish people have access to Mobile devices and 17% of those people have Internet enabled devices.
Internet Affordability- Stage 3
The major ISPs are: TeleDanmark, Cybercity, Image Scandinavia,
Telia, Get2Net,and Orange. The largest ISP is TeleDanmark, which
is controlled by SBC/Ameritech. TeleDanmark is the only ISP known
to have American ownership. Get2Net claims 40% of business subscribers
through its wholly owned subsidiary UNI-C. A decisive factor for
the spread of the new services of the information society is the
tariffs on the use of infrastructure. Many tariffs on telephones
in Denmark are relatively low compared to other Western countries.
The fact that there is a continued overpricing on especially the
international telecommunication connections is evident from the
explosive appearance of the so-called "call-back" operators
throughout Europe. Typically the "call-back" systems
originate in the United States, which has substantially lower
international tariffs than the European countries. Denmark - and
Europe in general - have a big problem in the shape of very high
tariffs on high-capacity data connections. Thus it is averagely
10 times as expensive to use the high-capacity networks in Denmark
compared to the United States
Network Speed and Quality-
Stage 4
Denmark is able to offer speeds that range from 56kbps to T1+
speeds to companies and home ISP users. Denmark is able to provide
quality network speed and quality because of its network infrastructure.
Most home users are able to access high speed networks from local
ISPs throughout Denmark. Overall the network speed and quality
should improve and become more affordable in the future. This
will allow the number of Danish network users to increase.
Hardware and Software- Stage
4
The total numbers of Personal Computers (PCs) in Denmark were
estimated at 3.1 Million by the International Telecommunication
Union (ITU) at the end of 2002, which included approx. 1.7 Million
Home PCs and 1.4 Business PCs, this figure increased by 29% since
1999. Total number of PCs per 1000 inhabitants, therefore, stood
at 575 in 2002, ranking Denmark in 4th place on a global list
of PC-usage.
Denmark is a highly computerized society with a huge demand for
highly sophisticated software. Denmark has a strong programming
tradition; both C++ and Turbo Pascal were developed by Danes.
Denmark is also considerably strong in the financial information
management systems. However over 85% of the software industry
is dominated by US companies, although German SAP has a strong
influence in Denmark industry. The US companies that have a strong
influence in Denmark are Microsoft, Oracle, and Lotus Notes.
Service Support – Stage 3
One of the biggest constraints on IT service and support in
Denmark is a lack of qualified IT personnel. According to the
Danish Institute of Technology, Denmark will be in need of as
many as 20,000 qualified IT-workers in the next few years. Denmark
tries to compensate their lack of IT workers by recruiting IT
specialists from Asia and Eastern Europe. Some countries outsource
their IT services and support to help increase their ability to
provide proper support. Denmark has struggled in recent years
to outsource IT services. Just recently in 2003, an outsourcing
agreement was signed to outsource most of the SAS and complicated
ticketing systems in Denmark.
The service and support provided in Denmark needs improvement,
however in the near future IT outsourcing will allow Denmark to
improve their IT services.
|
|

