| Overview |
| Network Access |
| Network Learning |
| Network Society |
| Network Economy |
| Network Policy |
| Conclusion |
 |
|||||
|
Overview |
|
||||
| The Hashemite King Dome of Jordan | ||||
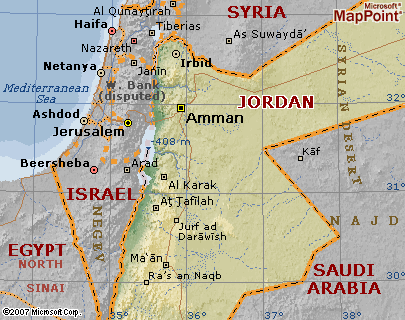
| In 1921 Emir Abdullah ibn Al-Hussein secured recognition for the Emirate of Trans-Jordan that became fully established in 1923. Fully independence came on May 25, 1946. In 1950 it became Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. Jordan, a young country dense with history, full of natural wonders and historical sites, is Located on the Southwestern Asia, situated near the south-eastern coast of the Mediterranean sea, bounded on the north by Syria, on the east by Iraq and Saudi Arabia, on the south by Saudi Arabia and the Gulf of Aqaba, and on the west by Palestine and Israel. The capital is Amman. The climate depends on which part of the country you are in, as altitude ranges from 400 meters (1,312 feet) below mean sea level at Dead Sea, to 1850 meter above sea level at the Al-Shirah Mountains. The climate tends to be dry during summer, while winter and spring are cooler, June to September are the hottest months of the year where temperature rises to about 32oC (89.6 F). The population of Jordan (2007 estimate), is 6,053,193, yielding an average population density of 66 persons per sq km (170 per sq mi). |
||||
| Geography | ||||
| Area: 89,342 sq. km. (34,495 sq. mi.). Cities: Capital--Amman (pop. 1.9 million). Other cities--Irbid (272,681), Az-Zarqa (472,830). Jordan is a relatively small country situated at the junction of the Levantine and Arabian areas of the Middle East. The country is bordered on the north by Syria, to the east by Iraq, and by Saudi Arabia on the east and south. To the west is Israel and the occupied West Bank, while Jordanís only outlet to the sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, is to the south. Jordan occupies an area of approximately 96,188 square kilometers including the Dead Sea, making it similar in size to Austria or Portugal. However, Jordanís diverse terrain and landscape belie its actual size, demonstrating a variety usually found only in large countries. Western Jordan has essentially a Mediterranean climate with a hot, dry summer, a cool, wet winter and two short transitional seasons. However, about 75% of the country can be described as having a desert climate with less than 200 mm. of rain annually. Jordan can be divided into three main geographic and climatic areas: the Jordan Valley, the Mountain Heights Plateau, and the eastern desert, or Badia region. . |
||||
| Government | ||||
| Type: Constitutional monarchy. Independence: May 25, 1946. Constitution: January 8, 1952. Branches: Executive--King (chief of state), Prime Minister (head of government), Council of Ministers (cabinet). Legislative--bicameral National Assembly (appointed Senate, elected Chamber of Deputies). Judicial--civil, religious, special courts. Political parties: Wide spectrum of parties legalized in 1992. Suffrage: Universal at 18. Administrative subdivisions: Twelve governorates--Irbid, Jarash, Ajloun, al-'Aqaba, Madaba, al-Mafraq, al-Zarqa, Amman, al-Balqa, al-Karak, al-Tafilah, and Ma'an. |
||||
| Economy | ||||
| Nominal GDP (2006): $14.3 billion. Annual real growth rate (2006): 6.4%. Per capita GDP (2006): $2,533. Natural resources: Phosphate, potash. Agriculture: Products--fruits, vegetables, wheat, olive oil, barley, olives. Land--10% arable; 5% cultivated. Industry (26.5% of GDP in 2006): Types--phosphate mining, manufacturing, electricity and water; cement and petroleum production, and construction. Trade: Exports (2006)--$5.17 billion: phosphates, potash, garments, fertilizers, pharmaceutical products, agricultural products. Major markets--U.S., Iraq, India, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., Syria, Israel, Kuwait. Imports (2006)--$11.46 billion: crude petroleum and derivatives, vehicles, machinery and equipment, cereals, fabrics and textiles. Major suppliers-- Saudi Arabia (mainly crude oil and derivatives), EU, China, U.S., Egypt, South Korea, Japan, Turkey |
||||