Appendix 1
Official Name: Russian Federation
Flag:

Capital City: Moscow
Major Cities: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Nizhni Novgorod, Novosybirsk, Ekaterinburg,
Samara, Omsk, Ufa, Chelyabinsk, Kazan, Perm, Rostov-on-Don, Volgograd
Population:
As of July 2004: 143,782,3381.3
Russia has been experiencing a slowly declining growth rate; in July of 2004 this number was estimated at -0.45% with a birth rate of 9.63 births/1,000 people and a death rate of 15.17 deaths/1,000 people1.3. In 2002 Russia’s official population was listed at 144.5 Million people with a -0.33% growth rate decline1.2. 148.2 Million were reported in the national census conducted in 19961.1. 82% of the population is ethnic Russians1.2.
Total Land Area:
In terms of total land area, Russia is the largest country in the world.
Total Area within borders: 17,075,200 sq km
Land Area: 16,995,800 sq km
Water Area: 79,400 sq km
Total Coastline: 37,653 km1.3
Bordering Countries:
Listed in alphabetical order along with total border length:
Azerbaijan 284 km
Belarus 959 km
China (southeast) 3,605 km, China (south) 40 km
Estonia 294 km
Finland 1,340 km
Georgia 723 km
Kazakhstan 6,846 km
North Korea 19 km
Latvia 217 km
Lithuania (Kaliningrad Oblast) 227 km
Mongolia 3,485 km
Norway 196 km
Poland (Kaliningrad Oblast) 206 km
Ukraine 1,576 km1.3
Administrative Structure: Federation of 89 states
Current President (as of 2004): Vladimir Putin
Religion: Religious preference depends on different ethnic groups however the Russian Orthodox Church comprises the significant majority1.2.
Language: Russian
Currency: Russian Ruble (RUR)
Education:
Approximately 98% of the Russian population over the age of 15 is literate.
The Russian constitution guarantees the right to free preschool, basic general
and secondary education until the age of fifteen. By 1995 Russia had 500 secondary
schools including 42 universities1.1.
Internet Country Code: .ru
Russia also has claim for the legacy domain .su which was allocated for the Soviet Union. It’s legal status and ownership are is under dispute between the Russian Government, ICANN, and several Russian commercial entities1.3.
Appendix 4.A
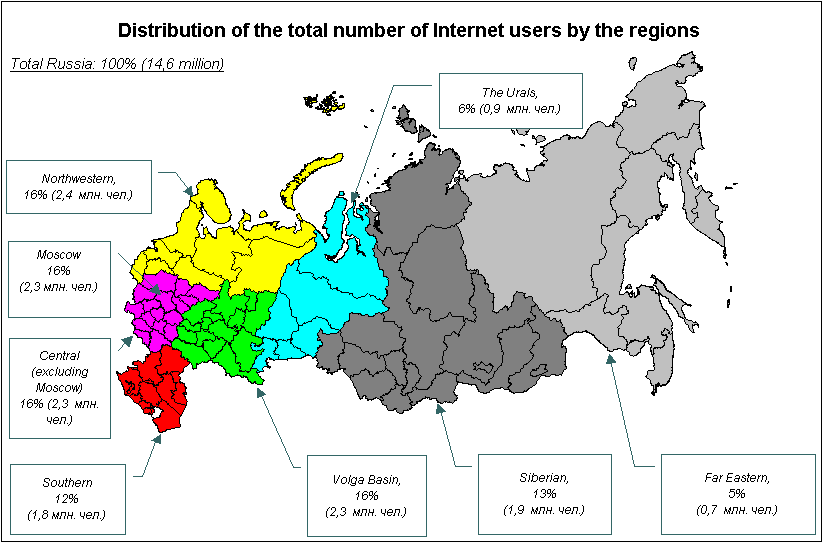
Appendix 4.B
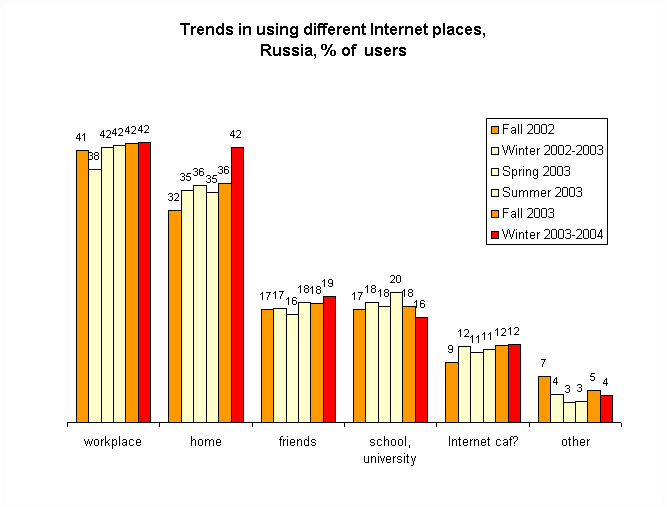
Appendix 4.C
http://www.psa.ac.uk/cps/2003/Marcus%20Alexander.pdf
Appendix 4.D
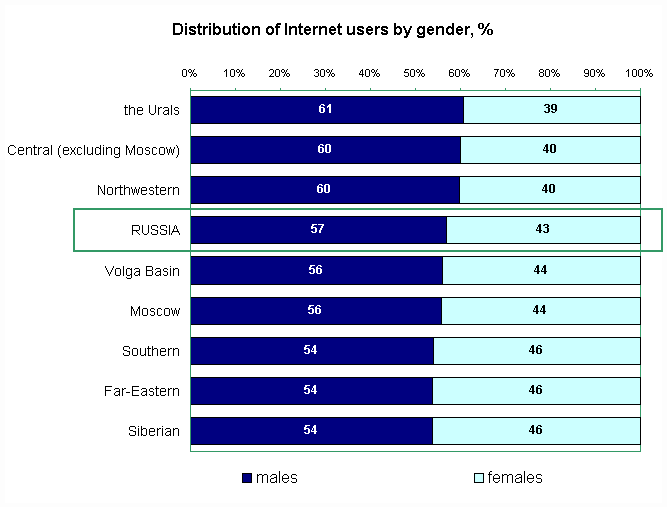
Appendix 6.A
Table of Russian Infrastructure Status
Infrastructure |
Liberalization Status |
Comments |
| Public Telecommunications Network | Monopoly | Russian Law on Communications |
| Local Networks for Voice Telephony | Partially Liberalizes Market | Russian Law on Communications |
| Leased Lines | Partially Liberalized Market | Russian Law on Communications |
| Alternative Infrastructure (railways, utilities, highways, etc.) | N/A | N/A |
| Broadcasting and cable TV | Partially Liberalized Market | N/A |
| Voice Telephony | ||
| Local Communication | Partially Liberalized Market | Russian Law on Communications |
| Domestic Long-Distance | Monopoly | Russian Law on Communications |
| International Communications | Partially Liberalized Market | Russian Law on Communications |
| Provision of voice services to closed user groups | Monopoly | Russian Law on Communications |
| Mobile Communications | ||
| Analog | N/A | N/A |
| GSM Digital | Partially Liberalized Market | Federal Providers: MTS, Vympelcom, and Megaphon |
| Paging | Partially Liberalized Market | More than 450 licenses |
| Satellite Communications | Partially Liberalized Market | Russian Satellite Communications Company (Gorizont and Express |
| Data Transmissions | Fully Liberalized Market | TCP/IP |
| Value Added Services | Fully Liberalized Market | N/A |
| Internet Service Provision | Fully Liberalized Market | N/A |
| Equipment Provision | Fully Liberalized Market | Article 16 of the Russian Law on Commercialization |
Appendix 6.B
Source: http://www.psa.ac.uk/cps/2003/Marcus%20Alexander.pdf
Appendix 6.C
Source: http://www.psa.ac.uk/cps/2003/Marcus%20Alexander.pdf