| Rio de Janeiro
Florianopolis
Sao Paulo
Blumenau |
Sao Paulo
CTI

Development
It was founded in 1982.
The facility is in progress to build a technological park much like
Polis at CPQD.
Advantages:
There appears to be a series of ongoing projects which are mostly
endorsed by the government. With more funding from government
allowing more interaction with academic institution
Financial
33% funded by government and 66% funded by private sector
It seeks out to create revenue by providing supplemental
courses for graduated incubators
Government funding will be audited on an annual basis.
Advantages:
Most of their funding is received on the federal funding which truly
help them grow and accelerate.
Competitive Advantage
Government funding gives this company an edge. Interaction with
graduated incubators allows CTI to maintain knowledge sharing when
innovated ideas arise at the academic institution.
Mainly focused on internal market
IT Policies
Itís main focus is Information Technology
3 areas of research and development: microelectronics, software, and
applications
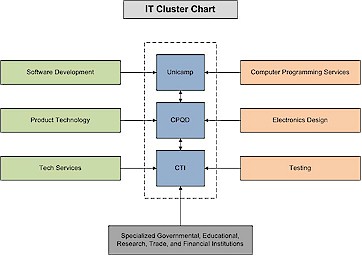
Collaboration takes place with several universities like USP, UNICAMP,
and UNESP
Collaborate with networks and companies like HP and Petrobrass
Everything is done here except Fabrication
Government
The federal government, a unit of the Ministry of Science and
Technology, is a key sponsor of CTI by providing financial support for
the organization and the public universities it partners with. The local
government is also involved in the project selection process to
meet social and developmental goals.
Advantages:
Most of their funding is attained at the federal level which provides
CTI more capability to work through the bureaucratic of Brazilian
government when seeking out for approval of the various projects they
are currently working on.
Disadvantages:
With heavy government funding, this create a longer delay process when
new projects are presented. For instance, their counterparts CPQD
with relatively bigger in mass size due to rapid expansion with private
sector funding while CTI will take a longer process to expand their
organization.
Challenges
Bureaucratic delays due to the involvement of the federal government in
selecting and funding efforts. Slower ability to expand or change to
new market conditions than private enterprise due to government control.
Developing new technology and skills to support and grow the changing
needs of Brazilian industry and people.
Administrative Issues
Their goal: liaison between academia and industry
Separate from UNICAMP, which creates a problem of rules and resources
Federal- cannot "invite" companies
Selection criteria of companies is still in process
1|2|3 |



