- Load the data from the CSV dataset into the data vectors r (Rating) and p (Price).
> setwd("c:/workspace") > getwd( ) [1] "c:/workspace" > data_frame <- read.csv("laundry-detergent.txt") > r <- data_frame$Rating > p <- data_frame$Price > r [1] 61 55 50 46 35 32 59 52 48 46 34 29 56 51 [15] 4 8 45 33 26 55 50 48 36 32 26 > p [1] 17 30 9 13 8 5 22 23 16 13 12 14 22 11 [15] 15 17 7 11 16 15 18 8 6 13 - Find the linear regression line for predicting Price from Rating.
> model <- lm(p ~ r) > model Call: lm(formula = p ~ r) Coefficients: (Intercept) r -2.1443 0.3727
The regression equation for predicting r from p is:
p = 0.3727 * r - 2.1443 - Create a scatterplot of Price vs. Rating. Add the regression line to this plot:
> plot(r, p, xlab="Price", ylab="Rating", + main="Laundry Detergent Dataset") > pred <- predict(model) > lines(r, pred, col="red")
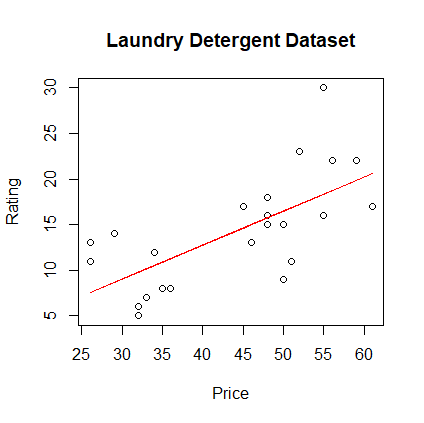
- Compute r and R2.
> # Correlation between p and r > cor(p, r) [1] 0.6707535 > # R-squared value > cor(p, r)^2 [1] 0.4499103
- Create a residual plot (plot residuals vs. predicted values). Add the
horizontal zero line.
> pred <- predict(model) > lines(r, pred, col="red") > res <- resid(model) > plot(pred, res, xlab="Predicted Values", ylab="Residuals", + main="Laundry Detergent Residual Plot") > lines(pred, rep(0, length(pred)), col="red")
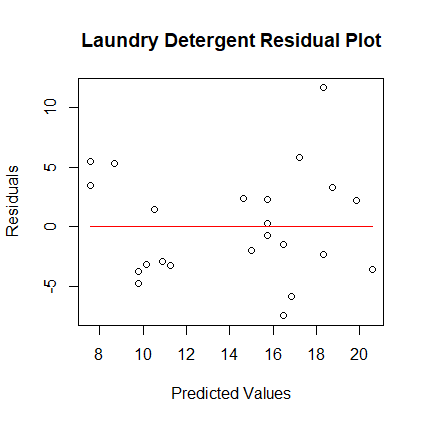
- Interpret the residual plot.
- Create a normal plot of the residuals with the normal line.
> qqnorm(res, main="Normal Plot of Residuals") > qqline(res, col="red")
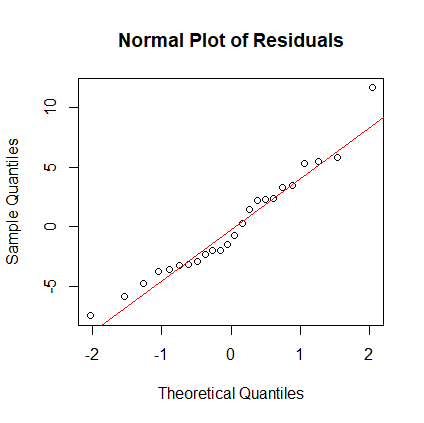
- Interpret the normal plot.
- Compute the height in meters and the weight in kilos of the Bears players.
The conversion rates are 0.3048 meters per foot and 0.4536 kilos per pound.
> setwd("c:/workspace") > getwd( ) [1] "c:/workspace" > bearsDf <- read.csv("bears-2024-roster.txt") > h <- (bearsDf$HtFt + bearsDf$HtIn / 12) * 0.3048 > h [1] 1.8796 1.9050 1.8542 1.9304 1.8542 1.8288 1.9558 [8] 1.8542 1.8034 1.9304 1.9050 1.9304 1.8288 1.8288 [15] 1.9304 1.9050 1.9812 1.9050 1.9558 1.8796 1.9304 [22] 1.8288 1.9050 1.9304 1.8034 1.8796 1.7526 1.8034 [29] 1.7780 1.9558 1.9812 1.8288 1.8288 1.8542 1.9558 [36] 1.8034 1.8288 1.9304 1.9812 1.8796 1.8288 1.8796 [43] 1.8288 1.8542 1.9304 1.8288 1.8034 1.8288 1.9304 [50] 2.0066 1.9558 1.8796 1.8796 1.7272 1.9050 1.7780 [57] 1.8542 1.9050 1.8288 1.8288 1.8034 1.9812 1.7272 [64] 1.8796 1.9304 1.7526 1.9558 > w <- bearsDf$WtLb * 0.4536 > w [1] 95.7096 96.6168 101.6064 136.9872 141.0696 105.6888 [7] 151.0488 90.7200 96.1632 108.8640 141.0696 139.7088 [13] 92.9880 90.7200 132.4512 136.0800 143.3376 143.3376 [19] 141.5232 134.2656 113.4000 109.7712 111.1320 99.3384 [25] 90.7200 108.8640 96.1632 90.7200 91.6272 145.6056 [31] 100.6992 88.9056 94.3488 102.0600 140.6160 86.1840 [37] 90.7200 121.5648 117.9360 136.0800 102.0600 109.7712 [43] 95.2560 90.7200 139.2552 104.7816 95.2560 88.4520 [49] 136.0800 150.5952 114.7608 91.6272 106.1424 79.3800 [55] 102.5136 83.9160 114.7608 129.2760 93.8952 92.5344 [61] 81.6480 118.8432 97.5240 95.2560 127.0080 81.6480 [67] 151.0488Find the simple linear regression equation for predicting weight in kilos from height in meters.
> model <- lm(w ~ h) > model Call: lm(formula = w ~ h) Coefficients: (Intercept) h -331.5 236.0
The linear regression line for predicting weight from height is
w = 236.0 * h - 331.5 - Use R to create a scatter plot of weight (y-axis) vs. height (x-axis). Add the regression line to the plot.
plot(h, w, xlab="Height (meters)", ylab="Weight (kilos)", + main="Plot of Weight vs. Height for 2024 Bears") > pred <- predict(model) > lines(h, pred, col="red")
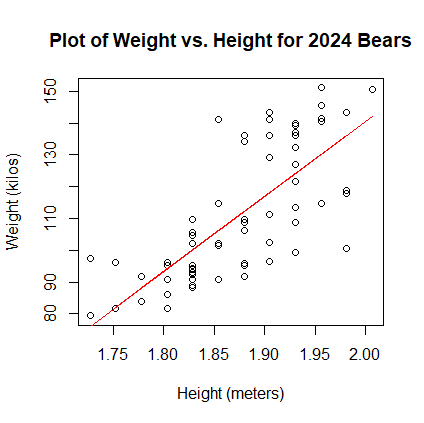
- Create the residual plot, which is the residuals (y-axis) vs. the predicted values (x-axis).
> res <- resid(model) > plot(h, res, xlab="Height (meters)", ylab="Residuals", + main="Residual Plot 2024 Bears") > lines(h, rep(0, length(h)), col="red")
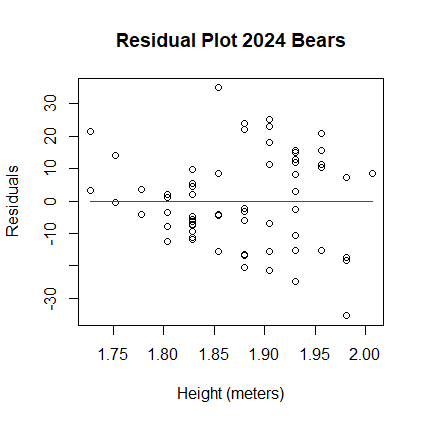
- Interpret the residual plot.
Answer: the residuals are slightly biased and heteroscedastic. - Create the normal plot of the residuals. Add the normal line to the plot.
> qqnorm(res, main="Normal Plot of Residuals 2024 Bears") > qqline(res, col="red")
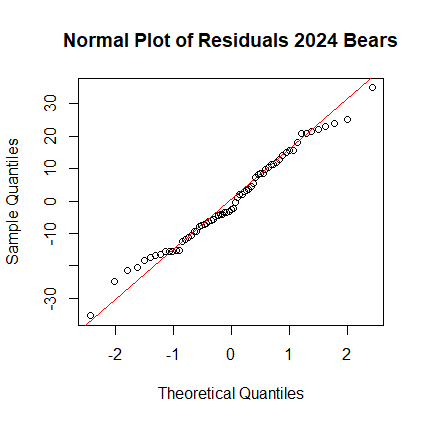
- Interpret the normal plot.
Answer: the normal plot shows small random variations above and below the normal line. This means that the residuals are approximately normally distributed.