| South Korea |
Country Profile |
||
Background: After World War II, a republic was set up in the southern half of the
Korean Peninsula (in August 15, 1945) while a communist-style government
was installed in the north. In June 2000, a historic first south-north summit took place between
the south's President KIM Dae-jung and the north's leader KIM Chong-il. In
December 2000, President KIM Dae-jung won the Noble Peace Prize for his
lifeling committment to democracy and human rights in Asia. He is the
first Korean to win a Nobel Prize. Geography of Seoul To the north of downtown is Bukhan Mountain, and to the south is the smaller Namsan ("South Mountain"). Further south are the old suburbs of Yongsan-gu and Mapo-gu, and the Han River. Across the Han River are the newer and wealthier areas of Gangnam-gu and surrounding neighbourhoods. Yeouido is a large island in the middle of the Han River, downstream from Gangnam-gu, and is home to the National Assembly, the major broadcasting studios, and a number of large office buildings. The Olympic Stadium, Olympic Park, and Lotte World are located in Songpa-gu, on the south side of the Han River, upstream from Gangnam-gu. South of the sprawling Gangnam area are Namhan Mountain and Gwanak Mountain. Urban and civil planning was a key concept when Seoul was first designed to serve as a capital in the 14th century. The Royal Palaces of the Joseon Dynasty still remain in Seoul, with the main palace (Gyeongbukgung) currently being restored to its original form.
Today, there exist 9 major efficient subway lines stretching for more than 100 kilometers which connects the greater Seoul Metropolian area, with a 10th line being planned. There are many significant streets to Seoul, but the most historically significant is Jongno - meaning the "Bell Street" - where 'jong' means a bell, and 'no' means a street. This bell that signalled different time of the day and therefore controlled the four gates to the city. It is still intact in its original form, and hit ceremonially at 0:00 every new years day. Seoul's most important streetcar line ran along Jongno until it was replaced by Line 1 of the Seoul subway system in the early 1970s. Other notable streets in downtown Seoul include Euljiro (À»Áö·Î), Sejongno (¼¼Á¾·Î), Chungmuro (Ã湫·Î), Yulgongno (À²°î·Î), and Toegyero (Åð°è·Î).
People
How
North and South Korea came to be
Korean Provinces 9 provinces (called do in Korean, singular and plural) Jeju-do (Cheju-do), Jeollabuk-do (Cholla-bukto), Jeollanam-do (Cholla-namdo), Chungcheongbuk-do (Ch'ungch'ong-bukto), Chungcheongnam-do (Ch'ungch'ong-namdo) Gangwon-do (Kangwon-do), Gyeonggi-do (Kyonggi-do), Gyeongsangbuk-do (Kyongsang-bukto), and Gyeongsangnam-do (Kyongsang-namdo).
7 metropolitan cities
(called gwangyoksi in Korean, singular and plural)
|
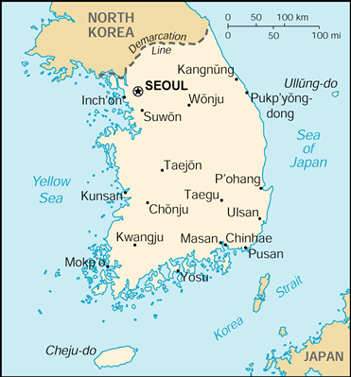
Official Name: Taehan-min'guk int'l long form: Republic of Korea int'l short form: South Korea abbreviation: ROK note: the South Koreans generally use the term "Han'guk" to refer to their country. Actual Time: Mon-Nov-15 14:15 Local Time = GMT + 9h Capital City: Seoul The Municipality of Seoul (pop. 11 million). Other Cities: Daejeon (Taejon, pop. 1.3 million) Taejon Metropolitan City Government. Incheon (Inchon, pop. 2.4 million) Incheon Metropolitan City. Gwangju (Kwangju, pop. 1.4 million) Kwangju Metropolitan Government. Pusan (Busan, pop. 3.9 million) Busan Metropolitan City. Daegu (Taegu, pop. 2.5 million) Taegu Metropolitan City Government. Government: Type: Republic with powers shared between the president and the legislature. Liberation: August 15, 1945 from the Japanese rule. Geography: Location: Korea is a peninsula country in Northeast Asia bordering China and Russia to the north, and Japan to the southeast. The Korean peninsula is surrounded by Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and East Sea (Sea of Japan). Area: 99,392 sq km (38,375 sq. mi.) (entire Korean Peninsula including North Korea: 222,154 sq km) (85,774 sq. mi.) Terrain: Partially forested mountain ranges separated by deep, narrow valleys; cultivated plains along the coasts, particularly in the west and south. Climate: Temperate, monsoon, four distinct seasons, and heavier rainfall in the summer. People: Nationality: Noun and adjective--Korean(s). Population 47,925,000 (estimate as of July 2003) Population growth rate: 0.6%. Ethnic groups: Korean; small Chinese minority. Religions: Protestantism 39%, Catholicism 13%, Buddhism 46%, Confucianism 1%, Cheondogyo (the Religion of Heavenly Way) and others 1% (Source: Korean National Statistical Office). Language: Korean, spoken by 70 million people and 5 million overseas Koreans. Writing system: Hangeul, the Korean alphabet, was invented by King Sejong the Great in 1443, consisting of 10 vowels and 14 consonants. Literacy rate: 97.75% (2000 estimate), male: 99.1%, female: 96.4% Natural resources: Limited coal, tungsten, iron ore, limestone, kaolinite, and graphite. Currency: Won (KRW) |