 Fig.
1
Fig.
1 NETWORK SOCIETY
People and Organization Online
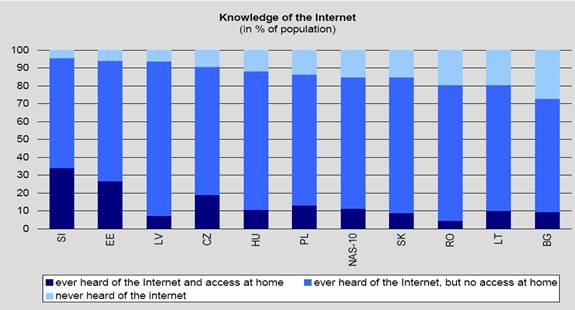
One of the main drivers for Internet growth is awareness – as more and more people are aware of what the Internet is and how to use it they become more willing to participate in it. The Czech Republic represents a very fresh and quickly growing Internet market and sector. Knowledge of the Internet is growing quickly according to recent studies. Approximately 20% of the entire Czech population has a considerable grasp of the Internet and its benefits and possibilities and have access at home while over 90% of the population has a grasp of the Internet however with no access to it. The figure 1 illustrates this statistic as compared to some of the other European countries. Internet use is also ranked quite high among the European nations. Almost 40% of the Czech population has a pc at home and is connected to the Internet. This promotes the use of the Internet and provides a viable network for research and general information searching. Figure 2 illustrates the study performed on Internet use in the household.
 Fig.
1
Fig.
1
Internet experience is largely a recent phenomenon. 14% of the Czech Internet users had their first encounter with the Internet in the past two years, and 16% had their first experience with the Internet more than two years ago. Figure 3 demonstrates a summary of the Internet Evolution in the Czech Republic as well as some other European nations.
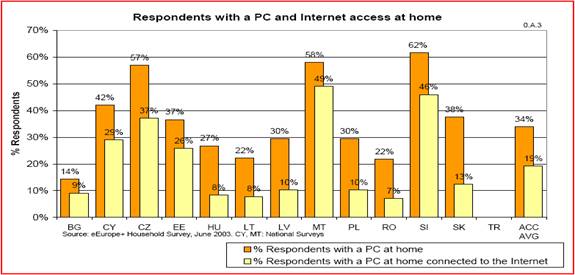 Fig.
2
Fig.
2
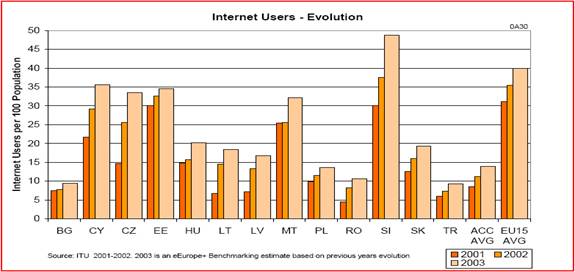 Fig.
3
Fig.
3
Based on these findings we can see the dramatic improvements that have taken place in the last two years. In 2001, the Czech Republic had approximately 14% Internet users. That figure nearly doubled in 2002 as over 25% of the population used the Internet regularly. In 2003 the amount of Internet users jumped just under 35%. This trend is continually changing as technological and digital tools are becoming more readily available to the public and Internet Access Points are stringing up all over major cities in the Czech Republic.
There has also been a concern that access to the Internet should not create a gender divide. Certain benchmarking surveys and studies have indicated that no such gender divide exists. Of the population participating in the study, 47% of Internet users were women and 53% were men. However the study did reveal that a gender divide does exist in the area of ICT related education. The parentage of women and men at the tertiary education level was 18% and 87% respectively. Due to this great diversity, certain steps have been taken to promote and encourage women to consider careers in the ICT field.
Locally Relevant Content
Community members find the Internet more useful and relevant to their own lives when the content reflects their own interests and needs. Locally relevant content is a major driver of growth of Internet usage. Interactions such as chat rooms, online forums, bulletin boards and web sites all drive the community to use ICT more widely in their lives.
We can classify the use of the Internet into the following categories: obtaining information, communicating with others, entertainment and selling and purchasing goods and services. The Czech Republic is very involved in a majority of these activities. In the field of obtaining information over 80% of the Internet users participate actively. Over 80% of the Internet users claim to communicate with others via e-mails, and approximately 20% use chat rooms and forums actively. The statistics concerning this field are displayed in figures 4 and 5.
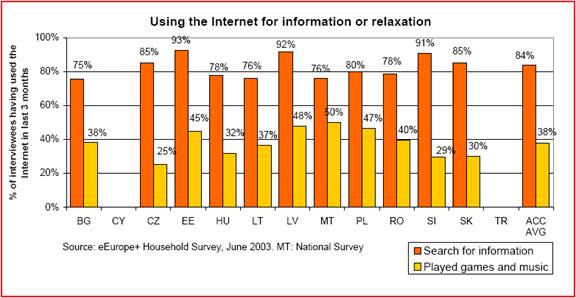 Fig.
4
Fig.
4
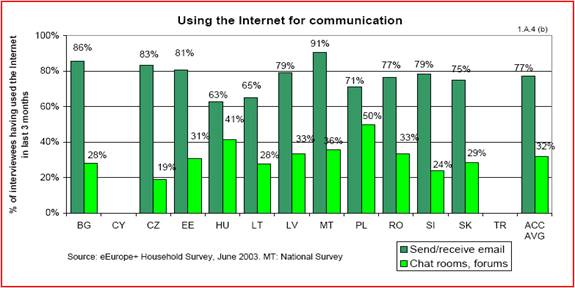 Fig.
5
Fig.
5
ICT in Everyday Life
Communities and individuals participate quite extensively in information and communications technologies. The telephone network is developed quite well not only in the Czech Republic but also throughout Europe. The development of the telecommunications industry has been rapid in recent years. According to the Czech Statistics Office, the number of telephone lines increased from 24 per 100 inhabitants in 1995 to 105 per 100 inhabitants in 2001. The number of mobile phone lines increased from 0.5 per 100 inhabitants in 1995 to 68 per 100 inhabitants in 2001. Based on that same study, 94% of young people under the age of 24 have a mobile phone in 2003. The use of mobile phones however diminishes among older age groups.
Rapid development in Internet use is also demonstrated. Based on a study performed in 2002, 80% of respondents to a survey between the age of 15 and 18 had access to the Internet, and 74% between the age of 19 and 23. Figure 6 below demonstrates some of the advancements that have been made in the field of ICT.
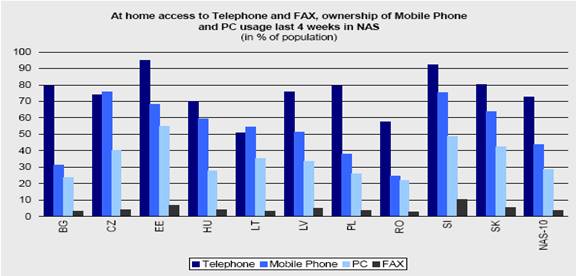 Fig.
6
Fig.
6
As was mentioned in section above, the Internet is a very familiar medium to the Czech population as well. Figure 1 illustrates that approximately 90% of the population is familiar with the Internet, its content and method of use. Over the past few years, there have been initiatives that try to introduce the Internet to the public. These events try to present the multi-faceted nature of the Internet. Topics such as e-education, e-government, e-commerce, and Internet access for the disabled people, the impact of the Internet and many others are presented to the general public.
When we focus on the particular use of the Internet, the use of e-mail is the favorite service used on the Internet. The number of people using e-mail in the Czech Republic is quite high among other European nations. 25% of the population uses e-mail for various purposes. Figure 7 demonstrates the intensity with which e-mail is used in the Czech Republic.
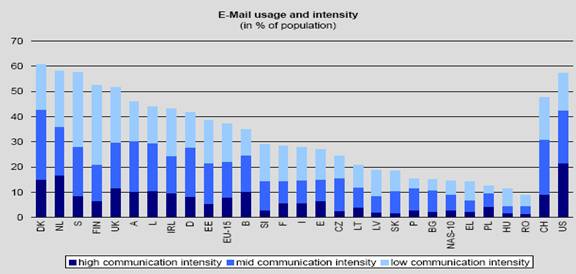 Fig. 7
Fig. 7
ICT in the Workplace
The more that businesses and government agencies use information and communications technologies, the better prepared they are to participate in the global network economy. The adoption of ICT into the workplace has not been as smooth and vibrant as other sectors and industries. The opposition by the workforce prevents from making smooth transitions into the digital workplace.
Slow progress has been made in the field as many organizations as well as the government is beginning to digitize content and information by providing database systems for information storage and the Internet and Intranets for information access and presentation. As displayed in figure 8 below over 60% of Czech enterprises report having a web site in place and operating whether for internal use or consumer communication.
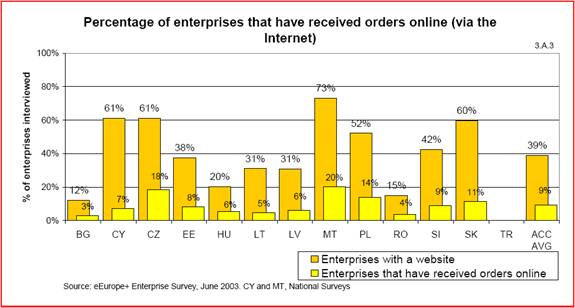 Fig.
8
Fig.
8
The Czech government has also made attempts to digitize its infrastructure by creating many of its offices and departments accessible online for public use. The Czech Republic government has made available the following e-services to the public although with mixed results. Not all services use the Internet as the preferred medium of performing and completing these services. The general public is still not quite comfortable accessing administrative services online. Based on the figure below, most of the services which are now accessible online are still being performed in the traditional manner, whether in person or through the mail. Fig. 9
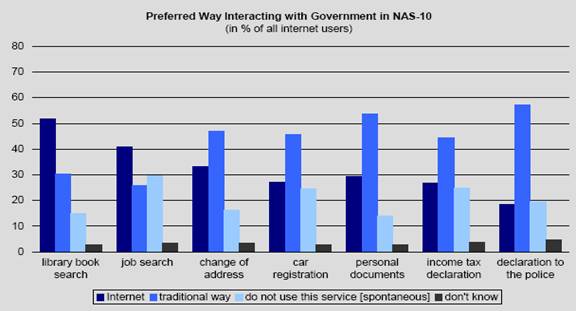 Fig.9
Fig.9
Conclusion
Based on the findings and evaluation of the network society in the Czech Republic we have reached a conclusion that currently the infrastructure and the development stage is approximately in the third stage, according to the CID Framework.
Based on the research we conclude that most of the population has heard and knows of the Internet, the content available and how to use it. Over 50% of the survey respondents claim that they use the Internet regularly. The majority of Internet users are not males between the age of 10 and 35. The gender divide in this case does not exist as just as many women as men use the Internet regularly. Advertising online has also become a very popular media for this type of communication to consumers.
Many websites are available in the local language, providing very dynamic, relevant and up-to-date information for all users catering to a very diversified community. The Czech Republic maintains its own domains in the native and local languages, while local web sites total into the millions. Local content is generated by citizens of all levels of society however as in the U.S. is dominated by the younger generation. Bulletin boards, chat rooms, forums are natural and numerous. As is displayed in the figures above, e-mail and information searches are the dominant activities for Internet users, followed by chat rooms, forums as well as online games and other forms of entertainment such as music.
Many members of the community use information and communication technologies. Approximately 20% of the Czech population owns personal computers. Of the computers connected to the Internet neatly 14% use a broadband connection. The mobile phone industry has seen extreme penetration in recent years. According to a study by the European Union panel, approximately 90% of the population is equipped with a mobile communication device such as a phone or a pager. European telecommunications is developed much better than in the United States. The networks, services and options offered with a basic mobile phone installation far exceed those that a mobile phone user in the Unites States will ever be offered.
A growing number of community members are beginning to utilize the Internet for purposes other than searching for information. A growing number of users are now interacting with the World Wide Web, by utilizing such services as e-banking and online shopping.
Organizations in the Czech Republic are slow to adopt ICT into the workplace. Opposition to change is quite high, as employees are reluctant to change the way in which work is performed. However advancements have been made as some organizations are beginning to realize the benefits and efficiencies which could be accomplished by implementing technology and digital tools into the workplace. Some employees conduct research and business transactions over the web, although most often a shared workstation is used to do so. Employees are however much more optimistic in regard to e-mail. This service allows employees an additional medium and means of communication among other employees as well as family members.
After examining these factors we have concluded that the Czech Republic currently resides in the 3rd stage of the CID development model.