Network Access
The Indian Telecom sector is passing through a dynamic transitional phase; it is clearly displaying the operation of market forces of demand and supply. The control of consumers is quite evident through their revealed preference in favor of economically rational decisions. The major policy reforms initiated since 1999 have resulted in the fastest ever expansion of the telecom network. The variety of telecom services being offered now to the users are amazingly vast. This has been possible because of opening up of all the telecom services for the private sector without any restriction on number of operators except for the cellular mobile phone segment due to frequency constraints. Private sector investment has been helping in bridging the resource gap to a considerable extent as was envisaged. In continuation of the initiatives taken in the past, several crucial policy decisions have been implemented during the current year.
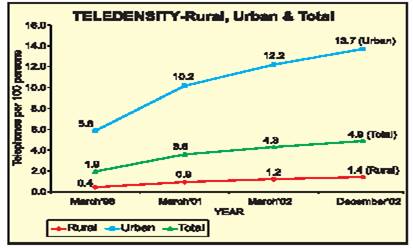
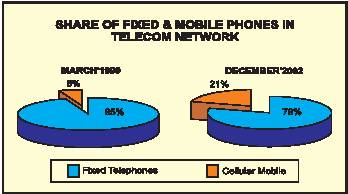
The phenomenal growth in the telecommunication sector after 1999 continued and during 2001-02 about 8.67 million new connections (5.71million by BSNL & MTNL and 2.96 million by private sector) were provided. The total telephone connections as on March 31,2002 were 45.0 million comprising 38.16 million fixed lines and cellular connections provided by BSNL & MTNL and 6.8 million by the private sector. By the end of December, 2002, the total number of phones increased to 50.93 million consisting of 41.27 million of the public operators and 9.66 million of private operators. The equipped capacity of the public sector unit (BSNL & MTNL) increased from 47.19 million lines as on March 31, 2002 to 49.77 million as on December 31, 2002. The basic Direct Exchange Lines (DELs) increased from 37.94 million to 39.48 million during this period.

The users preference in favor of Cellular Mobile Phones against fixed phones continued as CMPs grew by about 113% while the fixed DELs witnessed a negative growth of about 25% during the year 2002-03 (April-December), over the corresponding period of preceding year. Keeping in view the current trend during January–March 2003, about 4.5 million total new connections are expected to be provided and the growth rate shall be around 22% during 2002-03. The teledensity which was 4.3 percent as on March 31, 2002 has increased to 4.9 as on December 31, 2002.
As on December 31, 2002, there are 573 Internet Service Providers (ISPs)licensees out of which 24 ISPs have been given clearance for commissioning of 55 International Gateways for Internet using satellite media. Four ISPs have applied for setting up of Submarine Cable Landing Stations for International Gateways for Internet. BSNL has introduced Broadband services i.e. High Speed Internet Access, Video Broadcast, Video-on-Demand, Video Conferencing etc. at Kolkata as a franchisee based pilot project, utilizing BSNL’s Last Mile Copper Loop. This service is planned to be made available in 7 cities viz. Kolkata, Pune, Bangalore, Chennai, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad and Chandigarh during 2003-04.
Indian Internet Dimensions, 1988-1998
Today, INDONET connects eight cities via 64 Kbps leased lines. The entire network is backed up by redundant links provided by VSNL’s X.25 service, I-NET. Figure 4 depicts the current network. Today, one of the main services offered by INDONET is X.400 for electronic data interchange (EDI) and e-mail, with gateways to the global Internet in Calcutta and Mumbai. CMC is in the process of adding connections to Luck now and Vizag, providing additional links via the DoT’s High-speed VSAT Network (HVNET), and up-grading the network to TCP/IP.
The Education and Research Network (ERNET) was established by the DoE in 1986 as a multi-protocol network with seven other government organizations: NCST; the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore; and five IITs, in Chennai (Madras), Kanpur, Kharagpur, Mumbai, and New Delhi. The project received technical and financial support from the UN Development Program (UNDP). ERNET initially handled TCP/IP and OSI-IP traffic, but was converted to all-TCP/IP in 1995. The goals of the project were to set up a nationwide computer network for the academic and research communities, conduct research and development in computer networking, and provide networking training and consulting services.
|
ERNET Internet Fees |
|
|
Service |
Annual Fees |
|
Unlimited dial-up |
Rs 10,000 (US$246) |
|
Additional mail box (e-mail address) |
Rs 5,000 (US$123) |
|
Analog leased line |
Rs 110,000 (US$2,700) |
|
64 Kbps leased line |
Rs 310,000 (US$7,635) |
|
2 Mbps leased line |
Rs 2,510,000 (US$61,823) |
|
Wireless link |
Rs 510,000 (US$12,562) |
Internet Affordability in India is in stage 3 because the cost of Internet access is still high for some users even though there are a lot of ISP in the market. The cost of leased line for business is also extremely high. Flat rate pricing is still not available .
Today, the ERNET’s infrastructure comprises landlines within metropolitan areas and VSAT links between cities. The network comprises eight backbone sites and 104 VSATs(very small aperture terminals) , based on Hughes Network System (HNS) technology. The network hub, located in New Delhi, can maintain communications with each of five VSAT remote sites on each of 24 outbound channels. The total up-link bandwidth at the hub is 512 Kbps. The inbound links from the VSATs are time-division multiplexed into groups of 10 stations operating at an aggregate bandwidth of 128 Kbps. The system uses an INSAT-1D 22 dBW C-band transponder that supports one outbound link and 11 simultaneous inbound (VSAT to hub) links. The network uses the X.25 protocol as the carrier for TCP/IP traffic. The X.25 carrier is required because the VSAT network’s space segment uses a proprietary HNS protocol incompatible with TCP/IP. There are seven connections to the Internet via VSNL international gateways, of which five operate at 2 Mbps . The ERNET supports approximately 80,000 users at 700 organizations, carrying more than 10 GB of traffic daily. Approximately 12,000 ERNET subscribers are “serious” users who log on every day and use the Internet extensively. There are an additional 20,000 who use e-mail only.
|
Table 21. ERNET Gateways to the Internet |
|
|
Location |
Speed |
|
DoE, New Delhi (Delhi) |
2 Mbps |
|
Software Technology Park, Bangalore (Karnataka) |
2 Mbps |
|
VECC, Calcutta (West Bengal) |
2 Mbps |
|
NCST, Juhu, Mumbai (Maharashtra) |
64 Kbps |
|
NCST A-1 Building, Mumbai (Maharashtra) |
256 Kbps |
|
IUCAA, Pune, (Maharashtra) |
2 Mbps |
|
IITM, Chennai (Tamil Nadu) |
2 Mbps |
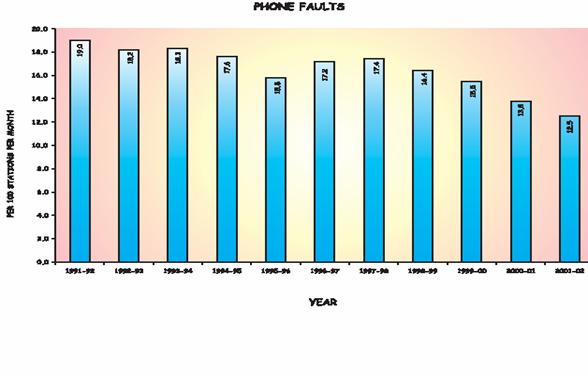
India is still in stage 3 in Network Speed and Quality due to phone fault and there is no high speed bandwidth offered in the residential area even though the connection between major cites is fast.
India’s main competitive advantage in software and services is its abundant, high quality and cost effective pool of skilled knowledge workers. Today, India is a magnet for software clients because of its vast resource of skilled software manpower. Since the inception of the IT industry in India, players within the country have been focusing on quality initiatives, to align themselves with international standards. The industry has set in place processes and procedures for offering world class IT software products and services. The focus on maintaining high quality has lead to an increasing number of companies getting assessed at key quality standards. As of December, 2002, India has 48
companies at SEI CMM Level 5 assessment. The quality maturity of Indian software and ITES-BPO industry can be measured from the fact that already 254 Indian software and ITES-BPO companies have acquired quality certification.
The domestic software market size continues to grow at a marginally lower rate, as compared with software services exports. The Indian domestic software market is likely to grow around 14 per cent during 2002-03, due to a slowdown in IT spending by the banking sector and manufacturing sectors.
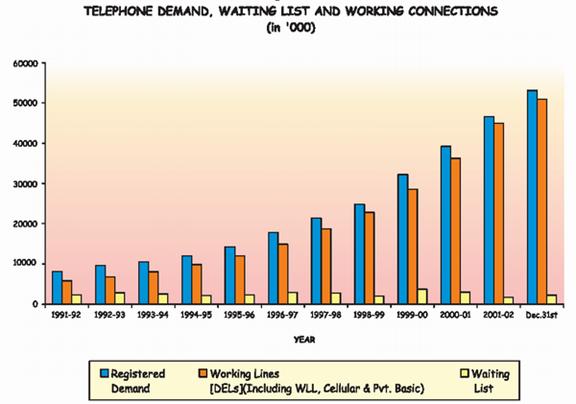
India is still in stage 3 in this category because it takes more than 3 months to complete the installation of mainline. Customer service between providers and users is still inadequate even though the new system such as Fault Repair/ Reporting System (FRS), Payment Reminder System (PRS), Customer Service Management System (CSMS) Change Number Announcement System. However, it is expected to improve in the next two years.
Recommendation:
India is still struggling to improve its infrastructure for the past decade, but the demand of users has extended beyond a core of networking professional. In order to meet the demand, India should be focusing on the following:
Increasing internet connectivity and enabling web-browsing and e-mail facilities
Improving interface between citizens and government
Enabling IT services including e-commerce
Drive the competition of Internet service providers by reducing the cost of license and allowing foreign direct investment into telecom sector
Increasing Internet usage and awareness to residential sector and business by providing flat rate pricing
Reference:
Dripto Mukhopadhyay . E-Readiness Assessment of States http://www.ncaer.org/Upload/others/94/Industry%20Briefs.PDF. 21 July 2003
Crisil Infrastructure Advisory. Private Sector Assessment – India http://www.adb.org/Documents/csps/ind/2003/appendix3_private_sector_assessment.pdf. Accessed 11/10/03
Anindo Ghosh. Private Internet Service Providers in India http://www.india50.com/isp.html#Anindo_Ghosh. 15 October, 1997
GUIDELINES AND GENERAL INFORMATION FOR INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDER(ISP) http://www.dotindia.com/tec/guidline.html
Annual report 2002-2003 http://www.dotindia.com/annualreport/annualreport.htm.
initial assessment: republic of india http://som.csudh.edu/cis/lpress/devnat/nations/india/gdi983.htm
Network Learning
Education is a joint responsibility of the Central and State Governments as per the Constitution of India, with funds for them provided by both levels of government and delivery of services largely a state responsibility. There are about 888,000 educational institutions in the country with an enrolment of about 179 nationwide. Elementary Education System in India is the second largest in the World with 149.4 millions children of 6-14 years enrolled and 2.9 million teachers. This is about 82% of the children in the age group.72 All States and Union Territories of India have adopted a uniform structure (the 10+2 system) of school education. Private sector participation in elementary education is expanding rapidly primarily because of the surging demand and the inability of the public system to deliver. Demand for private sector services are also increasing on account of the better quality associated with their services and increased parental ability to pay for such services. Private sector institutions are unlikely to emerge as significant direct contributors to the goal of universal education in the near future as their costs put them largely out of reach for the poor of India. They could however contribute significantly by reducing the pressures of the surging demand on the public system.
Vidya Vahini program proposes to integrate ICT in the learning environment in the
Government and Government-aided schools in the country. Under this program, a pilot
project has been undertaken in 140 schools in 7 districts in the country, namely, Kuppam
(Andhra Pradesh), Gandhinagar (Gujarat), Hazaribagh (Jharkhand), South 24 Paraganas
(West Bengal), Parlivaijnath (Maharashtra), Lucknow and Allahabad (Uttar Pradesh). The pilot project is being extended to district Barmer in Rajasthan. Each of the schools have been provided with one fully networked computer lab consisting of the following:
o One Server (P-IV based), 256 MB memory,40 GB Hard Disk Drive (Latest Technology available at the time),
o Network Printer,
o 10 Multimedia Personal Computer with Web Camera,
o 29” Colour TV,
o 2 KVA UPS with 15/30 minutes power backup and 1.5 KVA CVT,
o Software (MS Office full suite, Education software with Multi-lingual support, Course Curriculum software, Filtering software, etc
o Internet access of 128 Kbps through VSAT.
The entire system is scalable and has a 3-tier architecture. The personal computers in the
computer lab are connected to a server in the school which is further connected to a central portal and Internet.
‘Gyan Vahini’ Program proposes to upgrade the IT infrastructure at all the higher learning institutions in the country and connect them on Intranet and Internet to provide multiple education services within the institution. Each Faculty department including Administration, Finance, Hostel, Library and Laboratory will be connected on the High Speed Fiber Local Area Network (LAN). The focus of the project is to improve the quality of education and laying a good foundation at the higher learning institution and
encourage the institution and its affiliated colleges to share the resources, promotion and
implementation of e-governance, setting up a digital library, development of content, faculty development and exchange of skills. The program will encourage the teaching
community and students to develop content in the specialized areas to be made available to other institutions in the country. The whole program will enable the university to act as a resource centre and its affiliated colleges to exchange resources and skills. The project is envisaged to help better quality of education, world-class education, promotion and
implementation of e-governance, exchange of skills, knowledge and sharing of resources
among institutions, linkages with institutions all over the world.
The first pilot project has been implemented at Delhi University. A largest and state-of-the-art fiber optic based campus wide Local Area Network (LAN) has been set up at North Campus and the South Campus covering all the classrooms, laboratories, buildings and affiliated colleges situated in North and South Campuses. The two campuses have been interlinked thereby setting Intranet of University and colleges situated within the two campuses. The two LANs have then been connected to ERNET at CGO Complex using 2 Mbps leased links. Internet connectivity has been provided to this Intra-Net through ERNET Hub which in turn will be available to all users of this network. Similar project has been taken up to set up campus-wide network at Jamia Milia University, Delhi.
Under the project, review on existing back-end learning management software for digital
distance learning carried out. Course curriculum for M.Tech in courseware engineering and the short course on multimedia technology has been detailed out. CD-ROM based learning modules on – CBT on sound and audio technology, motion video technology (web format) and Java Programming (web format) have been developed.
Moreover, Department of Information Technology received 3,200 software packages during the year from Microsoft Corporation, under their program of providing academic software worth 1 million US $ every year for the children studying in various schools of the country. Each package contained MS Office, Visual Basic, MS Encarta, and MS School Bus Series (3 Titles). The software packages have been given to the various schools / trusts and Kendriya Vidyalayas and Navodya Vidyalaya. The software packages are given to the schools where the hardware is already available for running these packages.
The project aims to develop web based intelligent interactive tutoring system for four
basic engineering subjects viz., Physics, Chemistry, Mathematics and IT (Data Structures) and make the material available online to all engineering students throughout
the country. The multi-media rich content development for Mathematics and Data Structures is under progress at IIT, Delhi.
Employment Generation and Training Scheme (EGTS)
Department of Information Technology is implementing an Employment Generation and
Training Scheme for youths of North-Eastern States including Sikkim and for SC/ST/OBC candidates in other regions of the country. The overall objective of the scheme is to harness the potential of Information Technology in providing employment oriented training for the educated youth and to fill up the shortage of trained personnel in the North-East and other regions
Under the project design of user management, assessment, server management, query
management, session tracking and course management modules has been completed.
Componentization of these modules is under progress. the testing of these modules have been designed. Content Creation and Collaboration modules designs are under progress at Hyderabad, C-DAC. Two training programs aimed at training trainers in various e-learning related tools and technologies were conducted.