Network Access is divided into six categories which include Information Infrastructure, Internet Availability, Internet Affordability, Network Speed and Quality, Hardware and Software, and Service and Support.
Information Infrastructure
Lack of access to voice and data services is a significant hindrance for internet access in developing countries. Penetration varies based on geography, population, and income levels. Information infrastructure can be provided by physical and wireless media. For most developing countries, internet access is provided by traditional telecommunication networks however wireless access is becoming very attractive.
Brazil has the most developed information infrastructure in Latin America. It is heavily funded through incentives, regulations, and direct investments from the government. The fundamental goal of information infrastructure is to provide fast and efficient relay of information between two entities.
Brazil boasts a relatively large connected user base. When it comes to wireless telecommunications, this number represents roughly half of the population, about 100 million users. 25% of the Brazil's population access the Internet using one of approximately 8 million networked computers. This number continues to grow significantly every year.
Brazil continues to expand its information infrastructure to include the capability of launching communication satellites and experiments into space. They have a proven track record in the aerospace industry with Embraer, the largest and most recognized airline manufacturer in Brazil.
Internet Availability
Internet access is provided via many different services including dial-up lines, wireless technologies, and broadband offerings such as digital subscriber lines (DSL) and cable modem services. The types of services offered and the capacity of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) that operate locally affect availability. Additionally, public access to the Internet via internet cafes and community information centers play an important role in providing internet connectivity to people that do not have access at home, school, or work.
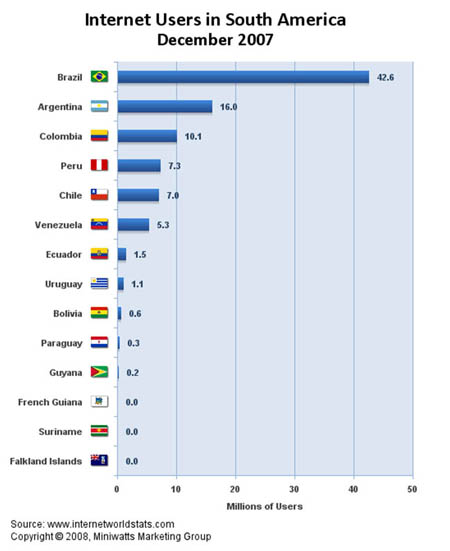
Brazil dominates South America with 42,600,000 users accessing the Internet followed by Argentina with 16,000,000 internet users. Brazil trails Argentina and Columbia in terms of penetration with only 22.4% of its population having internet access, according to InternetWorldStats.com.
Brazil's internet usage has grown over 750% since 2000 and continues to grow at an accelerated rate. This growth coincides with a migration from dial-up services to broadband services. ADSL is dominating the Brazilian broadband market with an 84% share, however most cable companies are offering broadband internet packages that are consuming the ADSL market.
The number of internet hosts has followed the same growth trend, breaking the 10,000,000 mark in 2008. Internet hosts are offering more services to compete in this growing market.
Internet Affordability
Fees charged for telephone usage and ISP services are used to determine the cost of internet access. If the prices businesses and individuals pay for internet access is relatively high, then the growth of network usage is constrained. Pricing structures can also affect networked activities. User's time online can be limited in areas where per-minute or hourly fees for internet and telephone service occurs. Providing tiered services can help improve affordability by allowing users to pay only for what they need.
Despite the considerable drop of internet access prices over the last ten years, a price reduction needs to occur to allow access for more people in Brazil. There are many factors that affect the affordability of network access including household income, location, incentive to invest in infrastructure, and government regulations.
Many people do not have access to the Internet at home because they cannot afford the cost associated with a computer. While computer costs are an issue, internet cafés are providing greater access for people who do not have a computer at home. In urban areas like Rio de Janeiro, internet cafes are almost as common as Starbucks are in the United States. Competition among the cafes has caused prices to drop and internet speeds to increase.
Brazil has made great strides in providing a market for affordable internet access which is prevalent in many of the cities in Brazil. There is a large number of Brazilians that do not have network access and the government needs to continue development and support of this growing market.
Network Speed and Quality
The speed of network access is affected by the amount of bandwidth the infrastructure can handle, the number of users, and their online activities. The quality of the network is also affected by the infrastructure. Not having a solid infrastructure can limit internet usage and discourage investments into new technologies.
One option for Brazilians to access the internet is using the 3G or Global Systems for Mobile communication (GSM) in Brazil. A major cell phone company (Celco) provider in Brazil is Claro. Over Claro's 3G network, they offer speeds from 500Kbps to 1Mbps. In order to access Claro's 3G network, the user must have a computer and either have a Universal System Bus (USB) port or a PC card (PCMCIA) port available.
Hardware and Software
The cost of hardware and software is very important for developing countries where low income households cannot afford the necessary equipment to obtain internet access. Retail distribution channels and a solid market help drive consumer costs down and encourage more specialized usage of networks.
High-speed internet does exist in numerous developed areas of the country and is accessible via a Celco, Telco, or a cable provider. Internet cafes are reasonably priced and very popular in Brazil. This does not apply to people living in favelas and in the northern part of Brazil, where internet access is difficult to obtain.
Service and Support
Customer service and support is important in assessing the readiness of a community. The quality and quantity of technical support professionals affects installation and repair times of network technologies. Lack of trained professionals can be a major issue for telephone and internet service providers.
Resources provided to research and educational institutions ensure a minimal shortage of internally skilled labor for the technology industry in Brazil. The government provides 73% of the funds for basic research and, when analyzing service and support, Brazil has an adequately skilled labor force to support IT organizations and operations.
The ability to find computer related services and support for Brazilians with computers is not difficult. Services are usually found in most cities and provided by vendors with storefronts along busy streets.
These storefronts provide support similar to that of Best Buy's Geek Squad in the U.S. and have prices most Brazilians consider high. However, some consumers enjoy cost savings overall when considering the utilization of open source operating systems and software.
[1] Competition and Globalization: Brazilian Telecommunications Policy at Crossroads
[2] Future of privatization and regulation in Brazil – What can be learned from the recent reforms?
[3] The Convergence of Telecommunications and Consumers Rights in Brazil
[4] Information and communications technology to Brazil
[5] Brazil: Building National IT Capacity for Domestic Market Development
[6] Appendix 3 National ICT Approaches: Selected Case Studies
[8] Network Wizards
[9] The Center for Research on Information Technology and Communication
[10] Internet Governance in Brazil
[11] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_in_Brazil
[12] http://www.budde.com.au/buddereports/1991/Brazil__Convergence_Broadband_and_Internet_Market.aspx
[13] For price on their 3G network
[14] Shows Claro’s coverage in Brazil
[15] Show’s amount of customer’s Claro has in Brazil
[17] Large provider of internet access in Brazil
[18] Computer in brazil
[19] Computer here
[20] Office 2007 Best Buy
[22] http://www.brasil.gov.br/ingles/about_brazil/brasil_topics/science/categoria_view
[23] https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/br.html
[24] https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/br.html
[25] http://www.alexa.com/data/details/traffic_details/orkut.com
[26] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Science_and_technology_in_Brazil
[27] http://www.space.com/missionlaunches/brazil_launch_041023.html
[28] http://www.inpe.br/programas/iss/ingles/default.htm
[29] http://www.brasil.gov.br/ingles/about_brazil/brasil_topics/science/categoria_view
[30] http://www.v-brazil.com/science/history-internet-brazil.html
[32] http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9E07E3DA1131F935A3575BC0A962958260