To ExamInfo Page
Final Exam Practice Problems 1
Multiple Choice Questions
For each question, show your work or give a reason explaining your answer.
4 points for the reason, 1 point for the correct answer.
- Roger Cotes was the first to publish a study on
- how well IQ scores fit the normal distribution.
- the applications of probability to economics.
- the theory of errors in astronomy.
- the uses of statistics in genetics.
Ans: c.
- Which of these is another name for categorical variables?
a. Continuous
b. Nominal
c. Ordinal
d. Scale
Ans: b. Nominal means that the data is not numbers. This is the
term used in SPSS.
- If Q1 = 1,230 and Q3 = 5,238, using the boxplot, the observation at
11,389 is
a. a mild outlier
b. an extreme outlier
c. below the 75th percentile
d. the median
Ans: a. IQR = 4,098. The inner fence to the right is at
Q3 + 1.5 * IQR = 11,385. The inner fence to the right is at
Q3 + 3.0 * IQR = 17,532. 11,389 is between the inner and outer fences,
so it is a mild outlier.
- What percentage of IQ scores are over 160,
assuming that IQ scores are normally distributed?
a. 0.32%
b. 0.032%
c. 0.0032%
d. 0.00032%
Ans: c: 0.0032%.
- For the curve shown below, the points shown in red are
a. asymptotes
b. critical points
c. inflection points
d. outliers
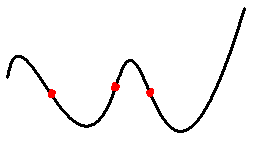
Ans: c: inflection points.
- The residual plot that we use in it223 consists of
- residuals plotted vs. normal scores
- residuals plotted vs. observation number
- residuals plotted vs. predicted values
- y-values plotted vs. x-values
Ans: c. Definition of residual plot.
Problems
Show all of your work. You may use a calculator.
- Compute the correlation of this dataset:
x: 1 2 3 4 5
y: 2 4 7 3 4
Here are the z-scores:
zx:
-1.414 -0.707 0.000 0.707 1.414
zy:
-1.195 0.000 0.000 -0.423 0.000
Ans: If SD+ is used to compute the standard deviations for the z-scores,
divide by n-1 when computing the average of the products zx*
zy.
r = (-1.414*-1.195 + -0.707*0 + 0*0 + 0.707*-0.423 + 1.414*0)
/ (5-1) = 0.2536
- Here are the summary statistics for the midterm and final scores in
a large class:
| average midterm score = 50; |
SD for midterm = 25; | |
| average final score = 55; |
SD for final = 15; | r = 0.60 |
Assume that the data are bivariate normal.
- About what percentage of students scored over 85 on the
midterm? Answer:
zx = (85 - 50) / 25 = 1.4. Using the standard normal table
Area(1.4,∞) = 1 - Area(∞,1.4) = 1 - 0.9192 = 0.0808 = 8.1%
- About what percentage of students obtained a score over 85 on the
final? Answer:
zy = (85 - 55) / 15 = 2.0. Using the standard normal table
Area(2,∞) = 1 -
Area(∞,2) = 1 - 0.9772 = 0.0228 = 2.2%
- Of the students that scored 85 on the midterm, what percentage
scored over 85 on the final? Answer:
Find the regression equation for
predicting final score from midterm score:
y - 55 = (0.6*15/25)*(x - 50)
y
= 0.36*(x-50) + 55
y = 0.36x - 0.36*50 + 55
y = 0.36x + 37
Also RMSE =
sy√(1 - r2) = 15√(1 - 0.62) = 15*0.8
= 12
A student that scored 85 on the midterm is predicted to score
y =
0.36*85 + 37 = 67.6 on the final.
What percent of students that scored 85 on
the midterm scored over 85 on the final? Answer:
z = (y - y^) / RMSE = (85 - 67.6) /
12 = 1.45.
Area(1.45,∞) = 1 - Area(-∞,1.45) = 1 - 0.9265
= 0.0735 = 7.4%
- Of the students that scored 25 on the midterm, what percentage
scored over 85 on the final? Answer:
z = (y - y^) / RMSE = (25 - 67.6) / 12 =
-3.55.
Area(-∞, -3.55) = 1 - Area(-∞,-3.55) = 0.0001926 = 0.019%
Simple Linear Regression
Perform the following analyses with R. Save your output file
as a Word .doc file. Type any interpretation of the output into the
output file itself.
- Input the R file.
tv-gpa.txt into R.
- Determine the following for Hours and HsGpa:
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
mean
SD+
Ans:
Using Tukey's Hinges for Percentiles
Hours: Q0=1.9
Q1=2.5
Q2=2.9 Q3=3.3
Q4=3.7
mean=2.871
SD+=0.5130
HsGpa:
Q0=2
Q1=5
Q2=9
Q3=14
Q4=14
mean=9.71
SD+=5.425
- Create the boxplot for Hours and HsGpa. Ans: Draw the boxplot by hand
or use R.
- Determine the correlation between Hours and Hspa. Ans: -0.0626
- Which is the independent variable? which is the dependent variable? Ans:
Hours, HsGpa
- Compute and interpret the r-squared value. Ans: 0.003919.
R2 is the
proportion of variation in the dependent variable that can be attributed to the
independent variable.
- Find the regression equation for predicting the dependent
variable from the independent variable.
Ans: HsGpa = -0.006 * Hours + 2.931
- What is the predicted highschool GPA for someone that watches
TV 40 hours per week. Why is this prediction not likely to be very
accurate?
Ans: 2.691. Because R2 is small.
- Create and interpret the residual plot. Use R.
- Create and interpret the normal plot of the residuals. Use R.
