CS 380/480 - Foundations
of Artificial Intelligence
- Winter 2007
Assignment
3
Due: Saturday, February 24, 2007
-
Suppose we have a knowledge base KB containing the following 5 sentences:
KB1: (A \/ B) /\ C => E
KB2 D /\ F => A
KB3: 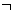 E \/ D E \/ D
KB4: B /\ C
KB5: F
- Using the inference rules for propositional logic and forward Chaining,
derive the sentence A. For each step indicate the rule applied and the
sentences used to derive the new sentence.
- Use resolution-refutation to prove that KB entails A (note: you will need
to first convert the sentences in KB to clause form).
-
Translate each of the following sentences into first-order predicate logic. Use the predicates defined below, but you
can also use additional
predicates, constants, or other vocabulary elements which you define yourself.
| Predicate |
Meaning |
| person(x) |
x is a person |
| course(c) |
c is a course |
| takes(x, c, t) |
student x takes course c during
term t |
| passes(x, c, t) |
student x passes course c during
term t |
| buys(x, y, z) |
x buys y from z |
| cooks(x, y) |
x cooks for y |
-
Some students took history in Fall 04.
-
Not everyone who took sociology, passed it.
-
Every student who passes both history and sociology, takes anthropology.
-
Only one student failed (did not pass) both history and sociology.
-
There is a person who cooks for all those who do not cook for themselves.
-
There is a broker who sells stocks to people who do not own any stocks.
-
Anyone who buys Google stock is a smart investor.
-
Consider the following sentences:
-
John likes all kinds of food.
-
Apples are food.
-
Chicken is food.
-
Anything anyone eats and isn't killed by is food.
-
Bill eats peanuts and is still alive*.
-
Anyone who is killed by anything is not alive.
-
Sue eats everything Bill eats.
-
Translate these sentences into formulas of first-order logic.
-
Convert the formulas into clausal form.
-
Prove that John likes peanuts using resolution.
-
Use resolution to answer the question "what food does Sue eat?"
-
Use resolution to answer (d), but, instead of the axiom marked with an
asterisk above, suppose we had the following:
-
If you don't eat something, you die.
-
If you die, you are not alive.
-
Bill is still alive.
-
Consider this knowledge-base for an instance of the Blocks World problem:
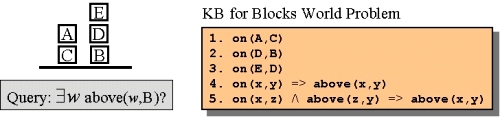
Use backward chaining (with Generalized Modus Ponens rule) to answer the query
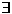 w above(w, B). Draw the complete
AND-OR proof tree showing all the answers to the query. [Note: for a similar
example, see slide 21 in Lecture notes: "Logical Inference and Reasoning
Agents".] w above(w, B). Draw the complete
AND-OR proof tree showing all the answers to the query. [Note: for a similar
example, see slide 21 in Lecture notes: "Logical Inference and Reasoning
Agents".]
- [Extra Credit] Implement the Unification Algorithm for sentences in
First-Order Logic (see Figure 9.1, Page 278 of Russell and Norvig).
[Project Idea / Extra Credit] Implement the Backward Chaining algorithm (see Figure 9.6,
Page 288 of Russell and Norvig).
Note: Extra Credit problems must be submitted separately from the assignment,
and by no later than March 11.
 Back to Assignments Back to Assignments
 Back to Main Page Back to Main Page
|

